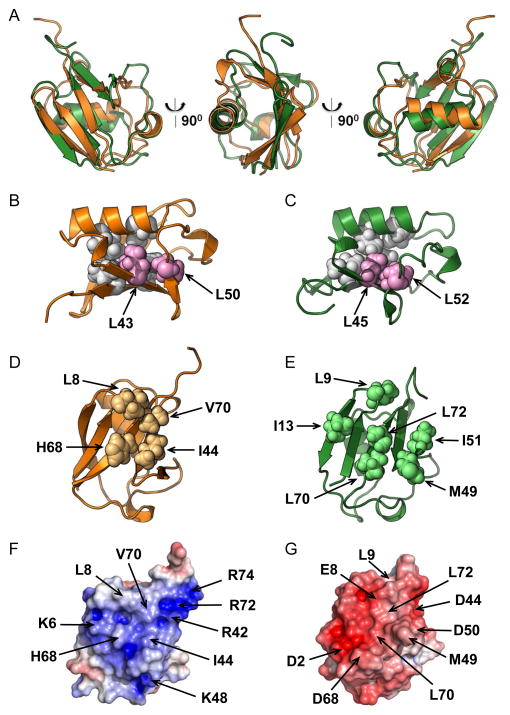
Figure 3.
Structure comparison of Ddi1UBL and Ub. (A) Cartoon representation of the overlay of 3D structures of Ub (orange) and Ddi1UBL (green). (B–C) Cartoon representation of the structures of Ub (B) and Ddi1UBL (C) with the side chains of the hydrophobic core residues conserved among all the UBLs (see Fig S1): L43, L50 in Ub (B) and L45, L52 in Ddi1UBL (C) shown as spheres, colored pink. Also shown in light grey spheres are several other residues that, together with the abovementioned residues form the hydrophobic core in Ub (V26, I30, L67, L69) and Ddi1 UBL (L28, L32, L71, I73). (D) Sphere representation of the hydrophobic patch residues on Ub surface. (E) Sphere representation of the residues on the surface of Ddi1UBL that form the hydrophobic surface patch. (F–G) Surface electrostatic potential (positive is blue, negative is red) of Ub (F) and Ddi1UBL (G), calculated using Adaptive Poisson Boltzmann Solver (APBS) (Dolinsky et al., 2004). The coloring range is ±4 kT/e for Ub and ±8 kT/e for Ddi1UBL. Both proteins are oriented similarly, with the β-sheet surface facing the reader. Location of charged side chains and major hydrophobic residues on the surface of each protein is indicated with arrows. (See also Fig S3)