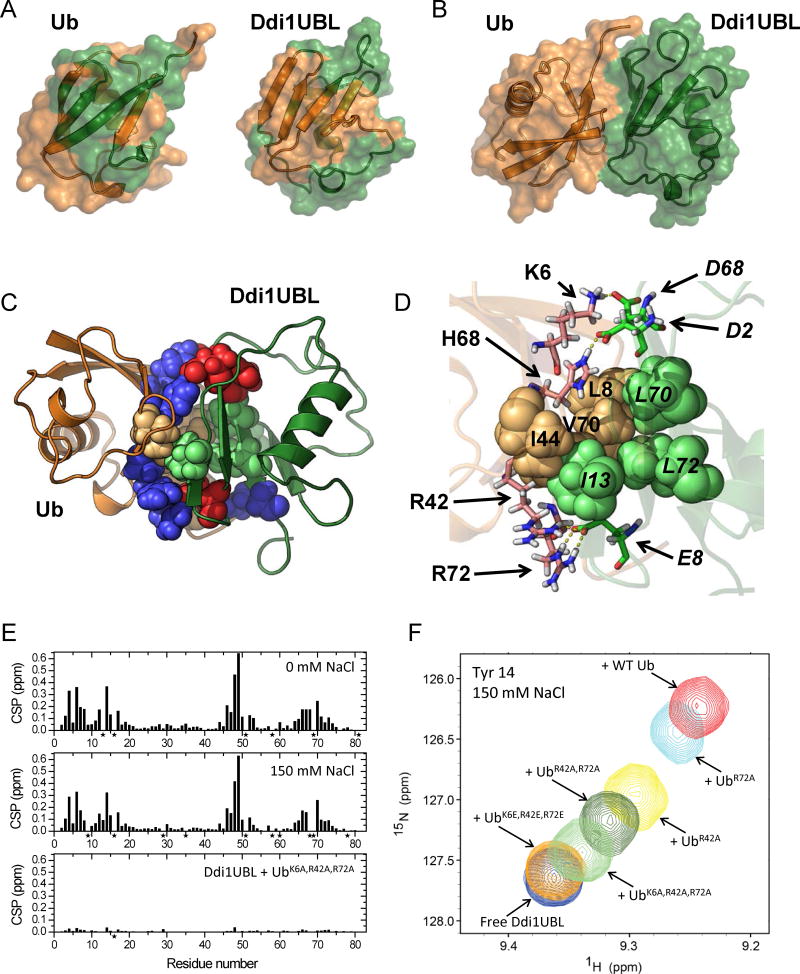
Figure 7.
Structure of the Ub:Ddi1UBL complex. (A) NMR-based mapping of the Ub:Ddi1UBL interface. Left: Ddi1UBL-binding site (colored green) on the surface of Ub (orange). Right: Ub-binding site (orange) on the surface of Ddi1UBL (green). CSPs > 0.075 ppm were used for mapping in both cases. (B) HADDOCK-derived structure of the complex of Ub (orange) and Ddi1UBL (green). (C) The Ub:Ddi1UBL interface is formed by both hydrophobic and polar/charged amino acids (shown as spheres colored orange and blue, respectively, for Ub, green and red for Ddi1UBL). Ribbon colors are as in (A–B). (D) Specific side-chain contacts at the interface of the Ub:Ddi1UBL complex. Hydrophobic amino acids of Ub: L8, I44, V70 (orange) and Ddi1: I13, L70, L72 (green) are shown as spheres. Shown in stick representation are K6, R42, H68, R72 of Ub (pink) and D2, E8, D68 of Ddi1UBL (green) that form polar/electrostatic contacts (shown as yellow dash lines). To distinguish between Ub and Ddi1UBL residues, the latter are indicated in italic. (E, F) Validation of the Ub:Ddi1UBL complex by measurements at physiological ionic strength and by site-directed mutagenesis. (E) Amide CSPs in Ddi1UBL at the endpoint of titration with WT Ub at 0 mM NaCl (top) and at 150 mM NaCl (center), and in the presence of 4-fold molar excess of UbK6A,R42A,R72A, also at 150 mM NaCl (bottom). (F) Overlay of the NMR signals of Tyr14 of Ddi1UBL free in solution and upon addition of WT Ub or indicated Ub mutants, at [Ub]:[UBL]=4 and 150 mM NaCl. (See also Fig S7)