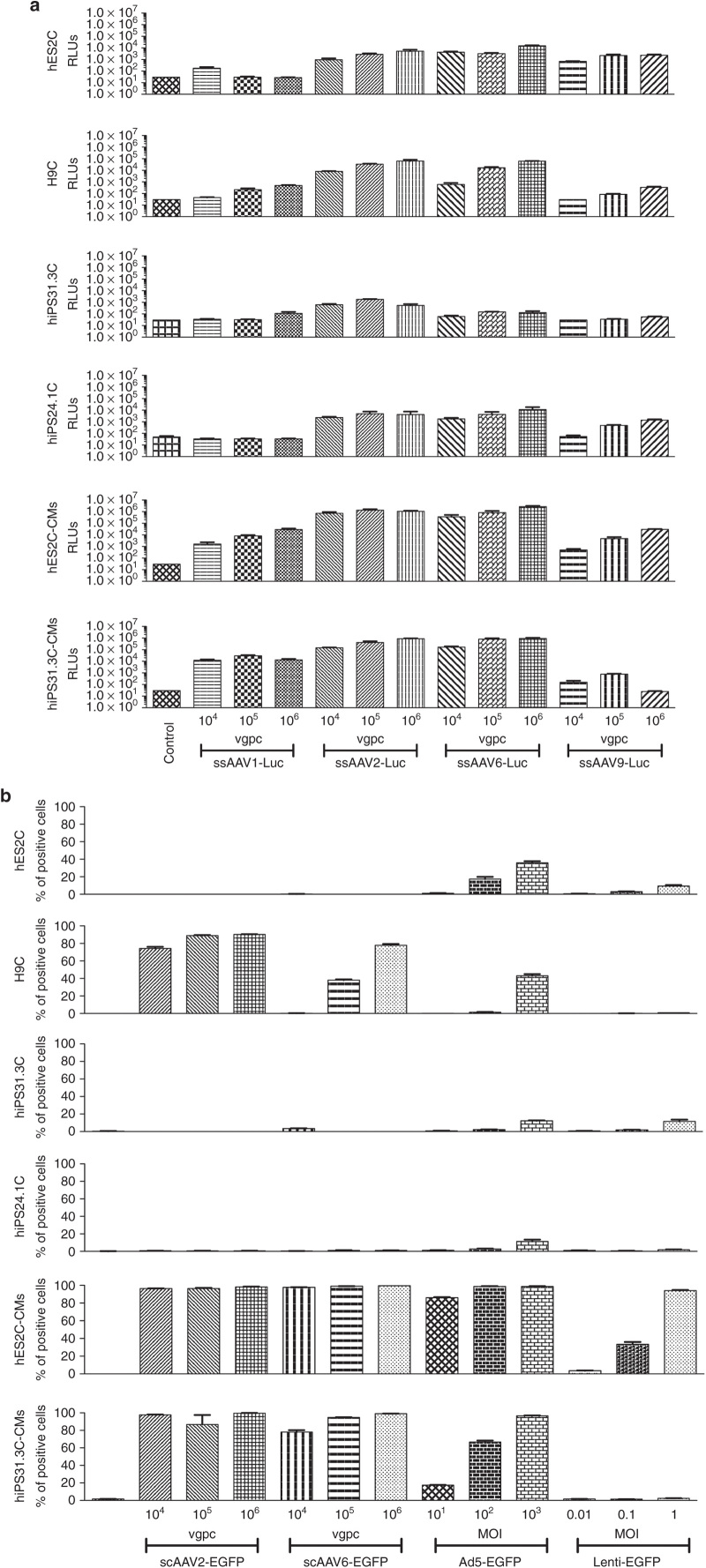
Figure 1.
Transduction efficiency by adeno-associated virus (AAV), adenoviral, and lentiviral vectors of different human embryonic stem cell (hES2, H9), human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPS31.3, hiPS24.1) lines, and hES2C- and hiPS31.3C-derived cardiomyocytes (hES2C-CMs and hiPS31.3C-CMs). (a) Luciferase assay was used to assess the transduction efficiency by four AAV serotypes (the cardiotropic serotypes 1, 6, and 9 and the archetypical serotype 2) of different pluripotent cell lines (hES2, H9, hiPS31.3, hiPS24.1) and cardiomyocytes derived from two pluripotent cell lines (hES2, hiPS31.3). AAV serotypes 2 and 6 appear to be the most efficient ones in transducing all cell types, with AAV2 showing higher efficiency in undifferentiated cells. In differentiated cells however, AAV6 is superior. In particular, in hES2C-derived cardiomyocytes, AAV2 is more efficient in lower concentrations (vg/cell), whereas at higher concentrations it saturates and AAV6 outperforms AAV2. Error bars depict ± standard error mean (SEM). (b) Flow cytometric analysis (% of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive cells) was used to assess the transduction efficiency by AAVs 2 and 6 (carrying self-complementary genomes), adenoviral (serotype 5) and lentiviral vectors. In undifferentiated cells, adenoviral and lentiviral vectors are superior to AAVs, whereas in differentiated cells (cardiomyocytes), the transduction efficiency of AAVs and in particular AAV6, is enhanced. Error bars depict ± SEM. Groups were analyzed by analysis of variance test. Please see Supplementary Table S1 (Luciferase, Figure 1a) and Supplementary Table S2 (Flow Cytometry, Figure 1b) for detailed statistical analysis. Error bars depict ± SEM.