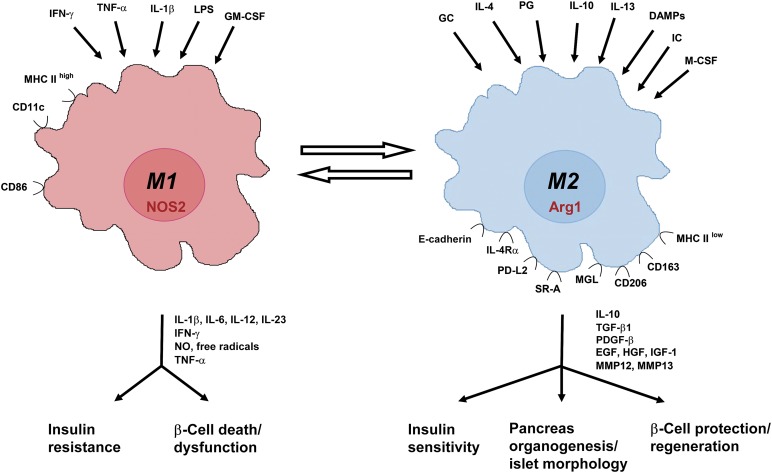
Figure 2.
M1 versus M2 macrophages: inducers, markers, effector molecules, and function. Summary of the most important inducers and markers of M1 and M2 macrophages and their role in pancreas development, insulin sensitivity, and β-cell death, dysfunction, and regeneration. Abbreviations: Arg, arginase; CD, cluster of differentiation; DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns; EGF, epidermal growth factor; GCs, glucocorticoids; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; ICs, immune complexes; IFN, interferon; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IL, interleukin; IL-4Rα, IL-4 receptor α; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MGL, macrophage galactose-type lectin; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PD-L, programmed death-ligand; PG, prostaglandin; SR, scavenger receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.