Fig. 7. ACD is sufficient to inhibit phagocytosis by J774 macrophages.
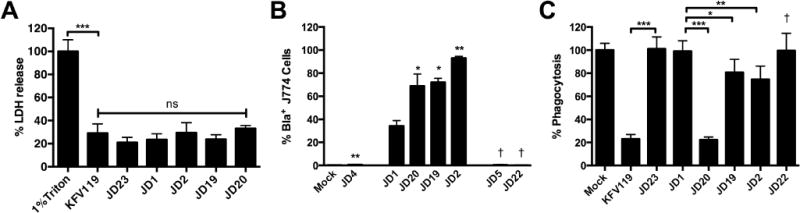
Cultured J774 macrophage cells were exposed to V. cholerae strain for 45 min and then assayed. (A) Percent cell lysis was determined as described in experimental procedures. (B) Translocation of Bla was quantified as shown in Fig. 3 with percent CCF2+/Bla+ cells from 10,000 cells shown as a histogram. (C) Percent phagocytosis was determined by uptake of fluorescent pHrodo Green E. coli Bioparticles. V. cholerae strains used in panel A (in order shown) are KFV119 (wild-type), JD23 (ΔrtxABCD), JD1 (rtxA::bla), JD20 (rtxA::acd-bla), JD19 (rtxA::rid-bla), and JD2 (rtxA::abh-bla). Additional strains in panels B and C are JD4 (rtxA::bla rtxB::km), JD5 (rtxA::bla C3568A), and JD22 (rtxA::acd-bla C3568A). Data shown in panels A and C are the average and standard deviation of three biological replicates while panel B represents biological duplicates. Statistical significance between samples indicated as determined by multiple comparisons after one-way ANOVA (**p<0.05 and ***P<0.005 are compared to rtxA::bla. †p<0.05 compared to paired sample without mutation)
