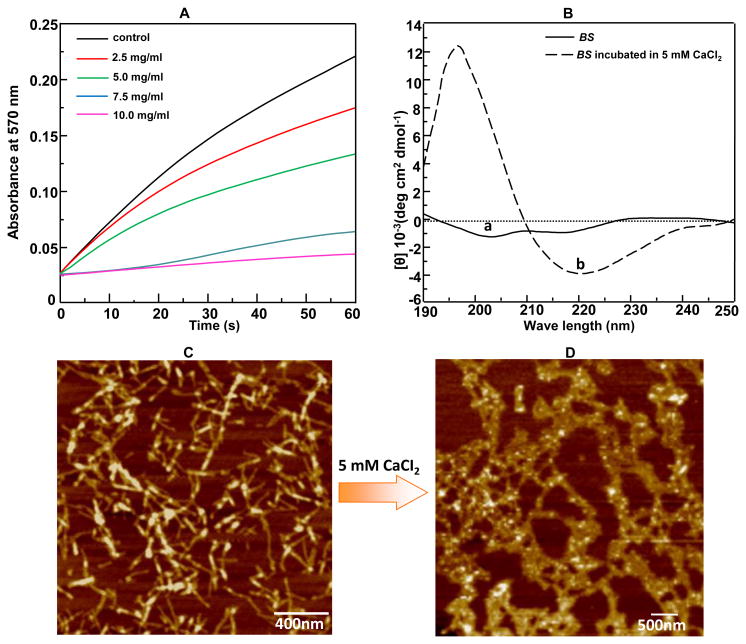
Figure 2.
Conformational change and self-assembly of BS in CaCl2 solution. (A) The Ca2+ binding ability of BS demonstrated by the decreasing absorbance at 570 nm of the mixture (made of 1.5 mL of 100 mM NaHCO3 (pH 8.7) and 300 μL of 20 mM Tris-HCl solution) in the presence of added BS with different concentration (0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10.0 mg/mL) after the addition of 1.5 mL of 100 mM CaCl2 (pH 8.7). The Tris-HCl solution (with NaHCO3 added but in the absence of BS) was used as a control. The stronger inhibition of precipitation of calcium carbonate, reflected by the reduced absorbance at 570 nm due to the inhibited calcium carbonate precipitation, indicated the higher Ca2+ binding activity. (B) CD spectra of aqueous BS solution before and after the addition of 5 mM CaCl2, respectively. The positive absorbance at 195 nm and negative absorbance at 217 nm indicated the appearance of β-sheet structure. (C-D) AFM image of the protein-based structures formed in aqueous BS solution before (C) and (D) after pre-incubation with 10 mM CaCl2 for 5 days.