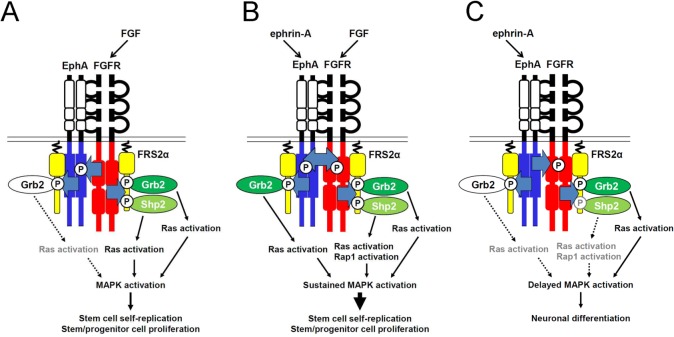
Fig 6. Schematic representation of EphA/FGFR/FRS2α complex signaling in NSPCs.
(A) FGF2-induced activation of FGFR leads to phosphorylation of both Grb2 and Shp2 binding sites on FRS2α. Both the Shp2- and Grb2-mediated pathways were found to lead to activation of MAP kinase via activation of the Ras pathway. Rap1 was not significantly activated. (B) Co-stimulation with FGF2 and ephrin-A1 induced strong and sustained activation of FRS2α. Both the Ras- and Rap1-mediated pathways resulted in quick and robust MAP kinase activation, augmenting self-renewal of NSPCs. (C) Ephrin-A1-induced activation of EphA led to delayed weak activation of MAP kinase, and appeared to be mediated mainly by the Shp2-Ras and Shp2-Rap1 pathways via trans-phosphorylation of FGFR by EphA. Activation of Ras through the EphA-mediated Grb2-Ras pathway was weak. Dotted lines and grey letters indicate decreased signals compared with solid lines and black letters. Two FRS2α molecules are included in the complex to conveniently separate the signal transduction pathways mediated by ephrin/EphA4 and FGF/FGFR. The binding stoichiometry has yet to be studied.