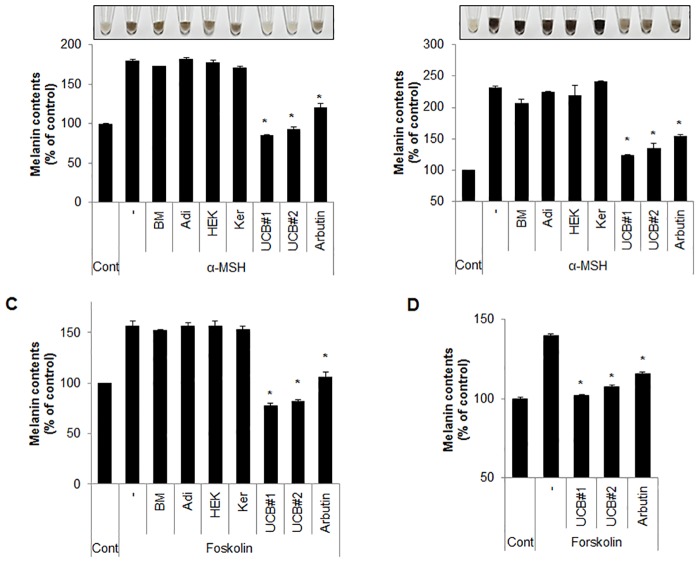
Fig 1. hUCB-MSC-CM suppresses α-MSH-induced melanogenesis.
(A) Melan-a cells pre-treated with α-MSH (1 μM) for 24 hr were incubated with BM (medium form bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells), Adi (medium from adipocyte mesenchymal stem cells), Ker (medium from human epidermal keratinocytes), and UCB (medium from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells) for additional 24 hr. Cells were treated with arbutin (500 μM) as an anti-melanogenic agent. Then, the cells were collected (upper image) to measure cellular melanin contents (lower graph) as described in the Material and Methods section. (B) B16F1 cells pre-treated with α-MSH (1 μM) for 24 hr were incubated with BM, Adi, Ker, UBC, and arbutin (500 μM) for 24 hr. Then, the cells were collected (upper image) to examine the cellular melanin contents (lower graph). (C) Melan-a mouse melanocytes pre-treated with forskolin (20 μM) for 24 hr were incubated with BM (medium from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells), Adi (medium from adipocyte mesenchymal stem cells), Ker (medium form human epidermal keratinocytes), or UCB (medium from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells) for additional 24 hr. Cells were treated with arbutin (500 μM) as a positive control. Then, the cells were collected to measure cellular melanin contents. (D) Normal human epidermal melanocytes were pre-treated with forskolin (20 μM) for 48 hr. The cells were further incubated with hUCB-MSC-CM or arbutin (500 μM) for 48 hr, and cellular melanin contents were measured. Data represent ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) from three independent experiments (n = 3,* p<0.02).