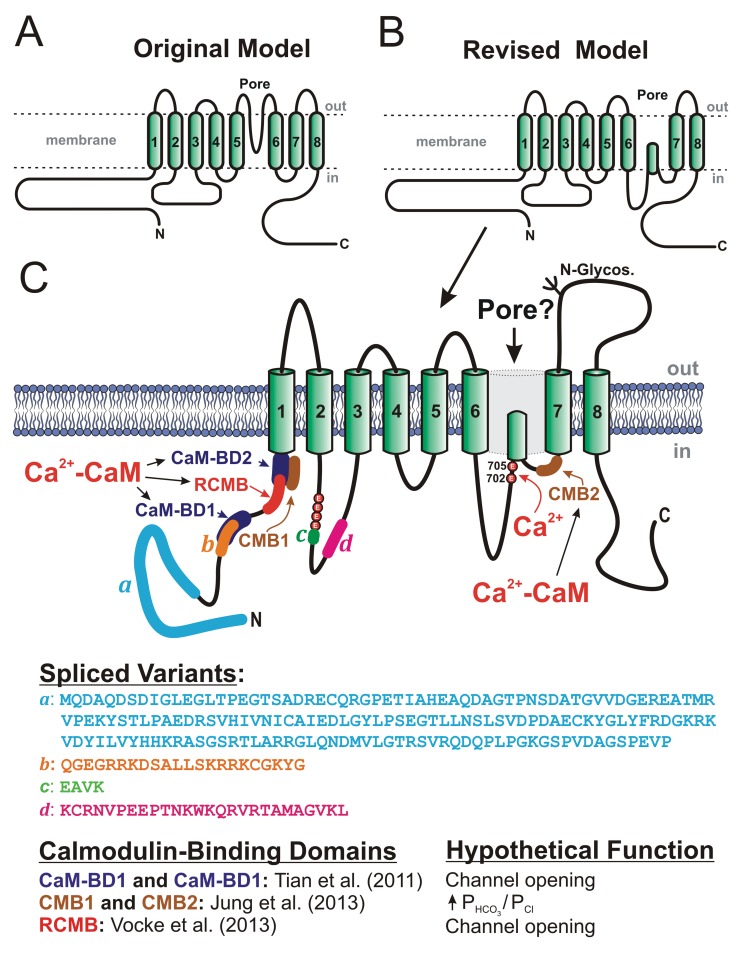
Figure 4.
Proposed secondary structures for anoctamin-1 (ANO1), or TMEM16A. A, Original model, based on predicted hydropathy profiles, describing the basic membrane topology of the protein, which comprises 8 transmembrane domains (TMDs), C- and N-terminal ends located in the cytoplasm, and a pore loop located between TMD5 and TMD6.13,15 B, Revised model proposing that the extracellular loop following TMD5 in the original model may instead face the cytoplasm.103 C, More detailed map of the revised membrane topology model of ANO1, revealing the locations and amino acid sequences of the 4 known spliced variants (a–d), the identification of 2 glutamate residues at positions 702 and 705 in mouse as potential Ca2+ binding sites,103 the location and hypothetical function of 3 classes of calmodulin (CaM)-binding domains (CaM-BD1 and CaM-BD2,104 CMB1 and CMB2,105 and regulatory CaM-binding motif [RCMB]106), and at least one N-glycosylation site (N-Glycos). The structure also exposes the location of 4 consecutive glutamate residues immediately proximal to spliced variant c, which were shown to be critical for Ca2+- and voltage-dependent gating of the channel.107