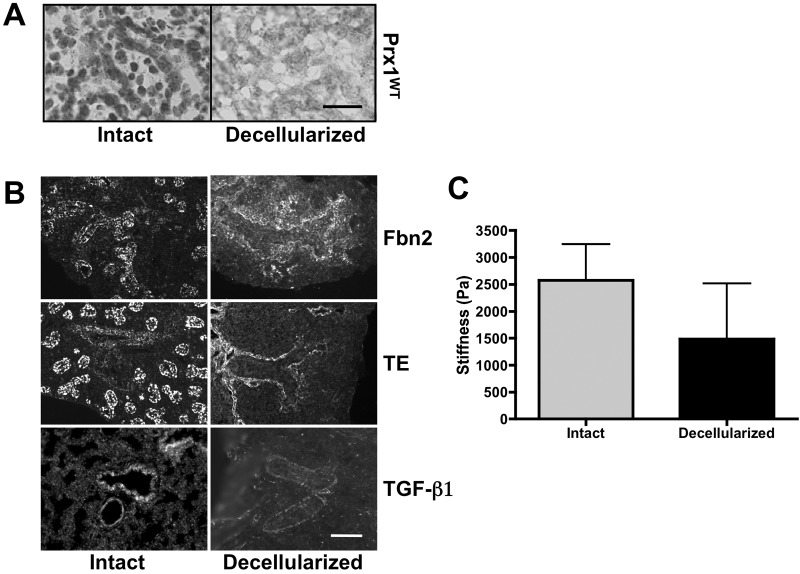
Figure 4.
Fetal lung extracellular matrix (ECM) is well preserved after decellularization. A, Hematoxylin staining for cell nuclei on frozen sections derived from intact (left) and decellularized (right) E17.5 Prx1WT lungs to confirm the removal of cells from tissue. Scale bar = 20 μm. B, Immunofluorescence staining for fibrillin (Fbn) 2 (top), tropoelastin (TE; middle), and transforming growth factor (TGF)–β (bottom) within intact (left) and decellularized (right) Prx1WT lungs to examine the preservation of elastic ECM components in decellularized ECM scaffolds. Scale bar = 20 μm. C, Stiffness (Young’s modulus) of intact and decellularized E17.5 Prx1WT lungs, determined by indentation testing. WT: wild type.