Figure 4. Inactivation of the PHP domain renders mycobacteria sensitive to nucleoside analogues.
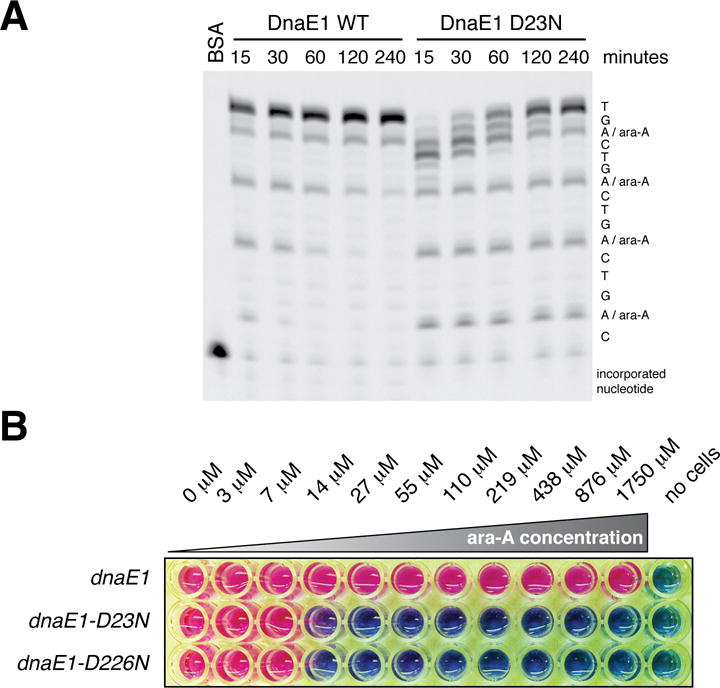
(A) Primer extension analysis performed as in Figure 1H in the presence of 200 μM of the adenosine analog ara-A. Incorporation of ara-A impedes primer extension. Whereas wild-type DnaE1MTB can excise ara-A and resume DNA synthesis, the PHP mutants cannot.
(B) Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ara-A for the indicated M. smegmatis strains. Pink color indicates cellular respiration; blue color indicates lack of respiration.
