Figure 2.
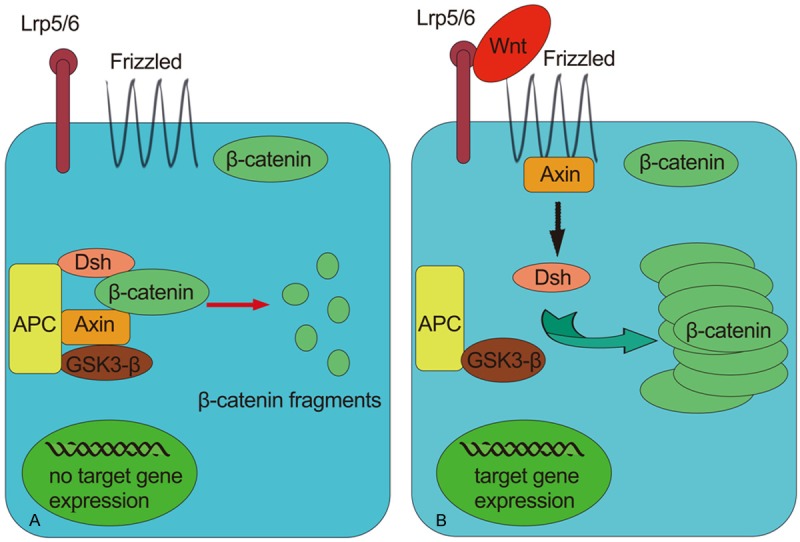
The activation of canonical (Wnt–β-catenin) pathway. A. In the absence of Wnt β-catenin is conventional phosphorylated by kinases CKI and GSK3 which are components of the destruction complex also consisting of APC and Axin. The β-catenin is subsequently degraded into pieces with no expression of Wnt target genes. B. The binding of Wnt to its receptors Lrp5/6 and Frizzled disintegrates the destruction complex. The interaction of APC and Axin or Dsh through an unknown mechanism puts a halt to the phosphorylation of β-catenins which are therefore accumulated in the cytoplasm and are then translocated into the nucleus and bind to Tcf/Lef, causing the expression of target genes.
