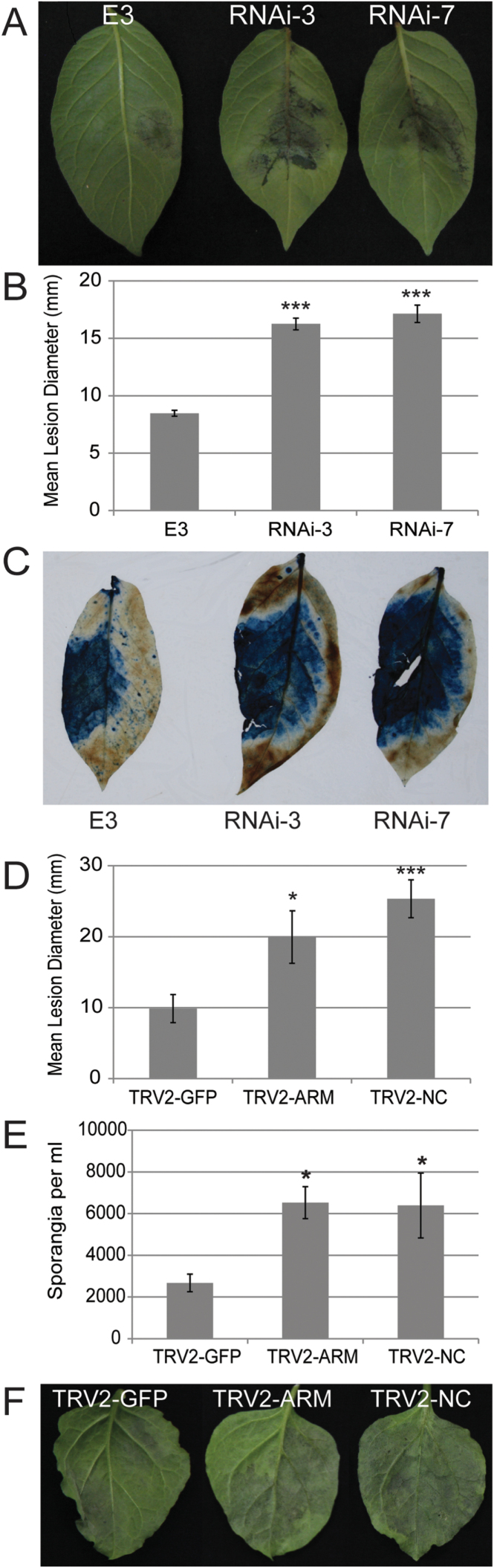
Fig. 1.
P. infestans colonization is enhanced by RNAi of StPUB17 in potato and by virus-induced gene silencing of NbPUB17 in N. benthamiana. (A) Representative images of leaves of the Control (E3) and StPUB17 RNAi potato lines at 4 d post infection (dpi) with P. infestans. (B) Graph showing mean lesion diameter at 4 dpi with P. infestans on the Control (E3), and the StPUB17 RNAi-3 and RNAi-7 potato lines. (C) Trypan blue staining of representative leaves of the Control (E3) and the StPUB17 RNAi-3 and RNAi-7 potato lines at 4 dpi. (D) Graph showing mean lesion diameter of P. infestans inoculations at 7 dpi on N. benthamiana plants silenced for NbPUB17 compared with the TRV-GFP control. (E) Graph shows the number of sporangia recovered ml–1 at 10 dpi from P. infestans-infected leaves silenced for NbPUB17 compared with the TRV-GFP control. (F) Representative leaves silenced for NbPUB17 and TRV-GFP at 10 dpi with P. infestans. Statistical analysis was carried out using ANOVA with pairwise comparisons performed with a Holm–Sidak test (Holm, 1979). Asterisks denote the P value as follows: *P ≤0.05, ***P ≤0.001; error bars show standard error. All experiments are the combination of at least three biological replicates, each using six or seven plants, and inoculations of at least four leaves from each plant.