Fig. 1.
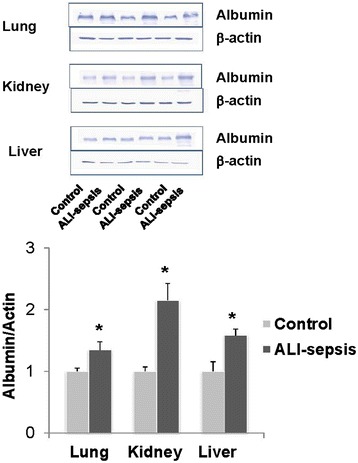
Increased albumin leak in the lung, kidney, and liver in an experimental acute lung injury-induced sepsis (ALI-sepsis) model. Combined Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia and mechanical ventilation in anesthetized mice was performed as previously described (Methods) [25]. Mice without any intervention served as controls. After 6 hours of treatment, the lungs, kidneys, and livers were harvested, flash-frozen, and stored at −80 °C. Western blot analysis of tissue albumin, top panel, was used to assess microvascular leak (Methods). Albumin and β-actin band intensities were measured from scanned membrane images by using ImageJ64 [54]. Albumin-to-β-actin ratios normalized to control tissues were calculated for each tissue; the graph depicts mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 mice in each group). *P <0.01 (t test) bottom panel
