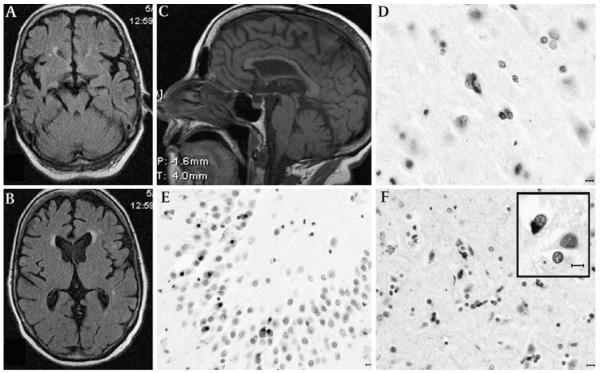
Figure 1.
Magnetic MRI and post-mortem findings of patient 1. Axial sequences at the midbrain (A) and thalamic (B) levels showing mild temporal- and frontal-predominant cortical atrophy; mid-sagittal T1 weighted MRI (C) demonstrates mild thinning of the body and genu of the corpus callosum with relative preservation of the splenium, suggesting a reduction of interhemispheric frontotemporal fibres; midbrain appears of normal size. TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) immunohistochemistry shows granular cytoplasmic deposits in the primary motor cortex (D). Neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions are abundant in the granule cell layer of the hippocampus (E). The subcortical white matter showed abundant pTDP-43 oligodendroglial inclusions (F). Some oligodendroglial inclusions had typical appearance of globular inclusions (GGI, inset). Horizontal bar=10 μm.