Fig 1.
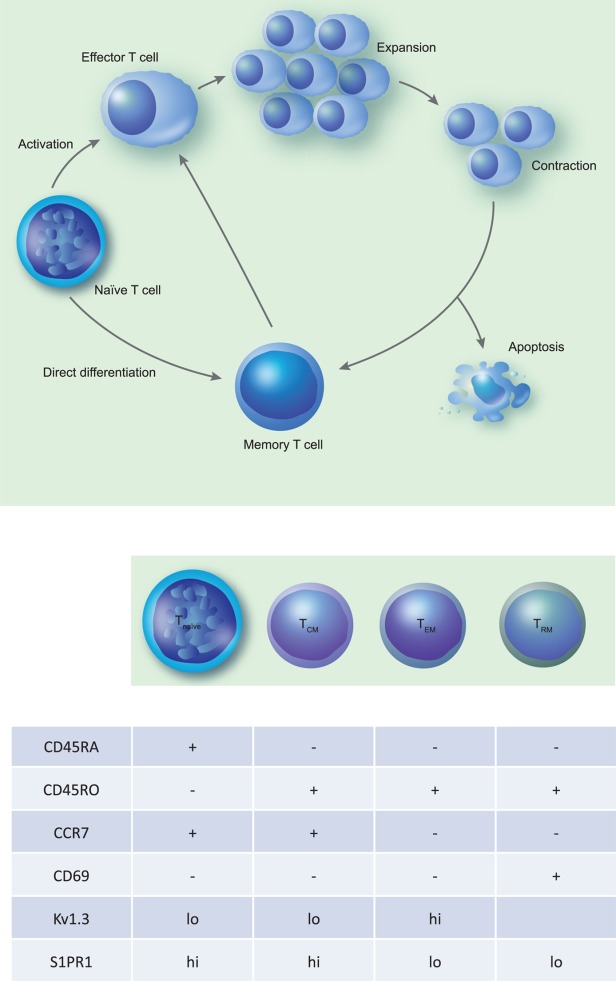
Generation of memory T cells and common surface markers of various subtypes of memory T cells. (a) The process of generation of memory T cells. Naive T cells undergo activation following engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) and appropriate co-stimulatory signals, subsequently undergoing proliferation and differentiation into effector T cells. Later in the immune response effector T cells undergo a contraction phase resulting in either apoptosis or differentiation into long-lived memory T cells. Additional pathways for generation of memory cells include direct differentiation of memory T cells from naïve cells and production of effector and memory T cells from naive cells by asymmetric cell division. (b) The common surface markers in tabular form used to identify the naive and memory T cells such as CD45RA, CD45RO, CCR7 and CD69. In addition, it lists some other markers that are expressed differentially on these cell populations and could potentially be used to target specific memory T cell populations.
