Fig 1.
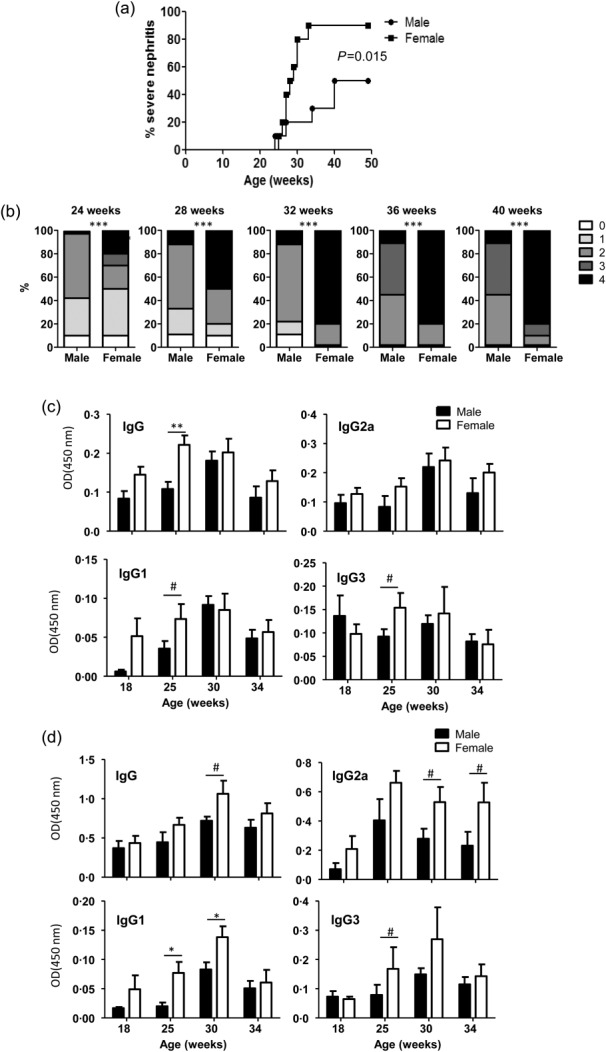
Gender difference in disease incidence and autoantibody levels in SNF1 mice. Male and female SWR × NZB F1 (SNF1) mice (10/group) were examined for proteinuria and autoantibodies. (a) Protein levels in urine samples were quantified by Bradford assay. Percentage of mice with severe nephritis as indicated by high proteinuria (≥5 mg/ml) is shown. (b) Severity of nephritis in male and female mice at different time-points is shown. Nephritis severity was scored based on urinary protein levels as follows; 0: 0–1 mg/ml, 1: 1–2 mg/ml, 2: 2–5 mg/ml, 3: 5–10 mg/ml and 4: ≥ 10 mg/ml. P-values were calculated using a two-tailed χ2 test. Serum levels of total immunoglobulin (Ig)G, IgG1, IgG2a and IgG3 antibodies specific against nucleohistone (c) or dsDNA (d) were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for indicated time-points. Each bar represents mean ± standard error of the mean of optical density values of samples from 10 mice/group.
