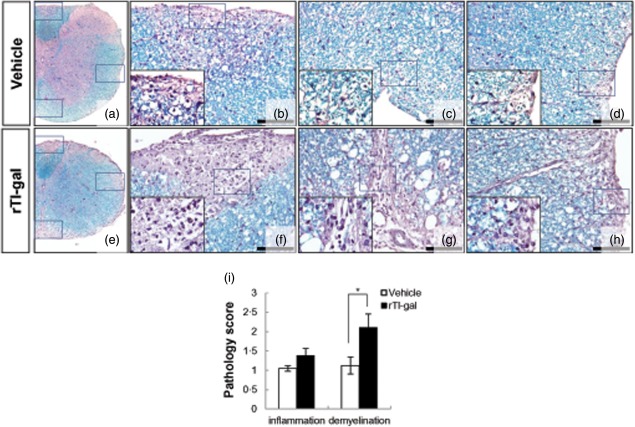
Fig 2.
Neuropathological changes within representative lumbar spinal cord sections obtained from recombinant Toxascaris leonine galectin (rTl-gal)-treated and control (vehicle-treated) mice. Inflammatory infiltration and a large plaque of demyelination were seen in rTl-gal-treated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice at chronic stage (60–62 dpi) (e–h). Images in (b–d) and (f–h) are higher magnifications of the boxed portions in images (a) and (e), respectively. Bars = 60 µm in (b–d) and (f–h). (i) Mice were subjected to histopathological assay. Each group consisted of three animals. Sections were analysed for haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and luxol fast blue staining to detect inflammatory infiltration and demyelination, respectively. Values represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). Statistical difference of P < 0·05 (*) for rTl-gal-treated mice versus controls is indicated.