Fig 4.
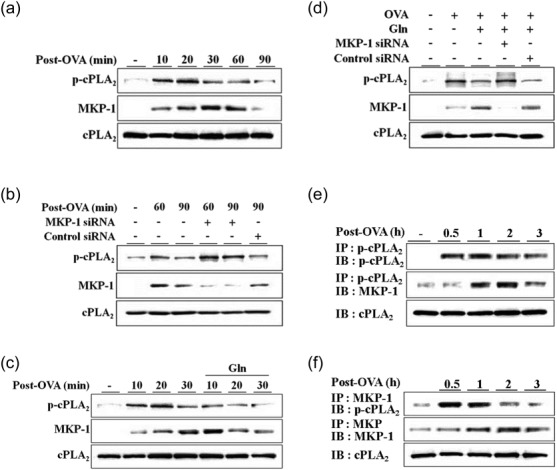
L-glutamine (Gln) deactivates phosphorylated (p)-cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) through mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in asthmatic lungs. After a second ovalbumin (OVA) airway challenge, lungs were removed at the indicated time-points (a–c). Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) (0·2 nM) were administered intratracheally (i.t.) 24 h before the second challenge (b,d). Gln (750 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) immediately after the cessation of the second challenge (c,d). Lungs were removed at 10 min post-challenge (d). Lungs were removed at the indicated time-points. Lung lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-p-cPLA2 or anti-MKP-1 antibodies (e,f). A representative of three to five independent experiments with three to five mice/time-point/experiment is shown.
