Figure 6.
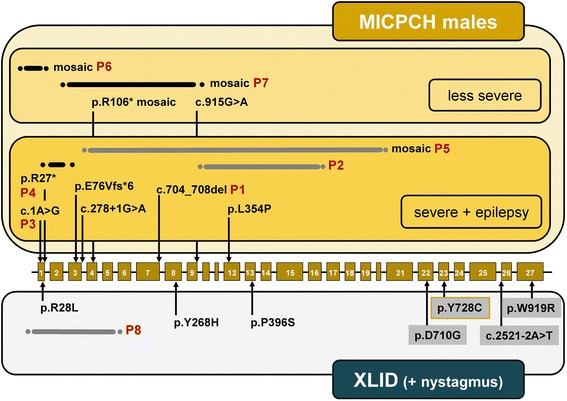
Summary of CASK mutations in males. Exons of CASK are represented as light brown boxes and introns as black bars. The exon-intron structure is not drawn to scale. CASK mutations are given at the nucleotide level (for variants affecting splicing and for variants for which the prediction on protein level is not possible) or protein level. The arrows point to the position of the mutation within the exon or intron. Duplications of CASK exons are represented by grey bars and deletions by black bars; dots indicate that the exact duplication/deletion breakpoints have not been determined. Mutations associated with microcephaly and pontocerebellar hypoplasia (MICPCH) with/without epilepsy are grouped above the exon-intron structure (yellow background); mutations in individuals with severe MICPCH with epilepsy and less severe MICPCH are differentiated by dark and light yellow background, respectively. Mutations in males with X-linked intellectual disability (XLID) are shown below the exon-intron structure (light grey background), those associated with nystagmus have a dark grey background. The yellow framed p.Y728C change was identified in two brothers, one with MICPCH and nystagmus and one with ID, microcephaly and nystagmus. P1-P8: Numbering of patients 1–8 as described in this study.
