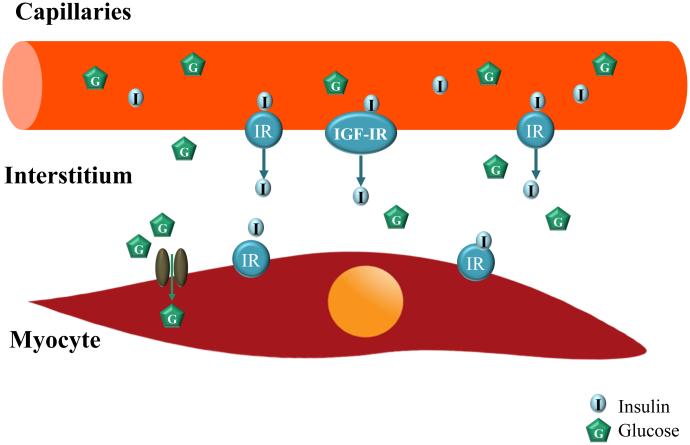
Figure 2. Transendothelial insulin transport.
To act on muscle cell insulin receptors, insulin has to be delivered to the capillaries nurturing the muscle cells and then transported through the endothelial barrier to reach the muscle interstitium. Insulin acts on endothelial cell insulin receptors (IR) and IGF-I receptors (IGF-IR) to facilitate its own transendothelial transport from blood to muscle interstitium.