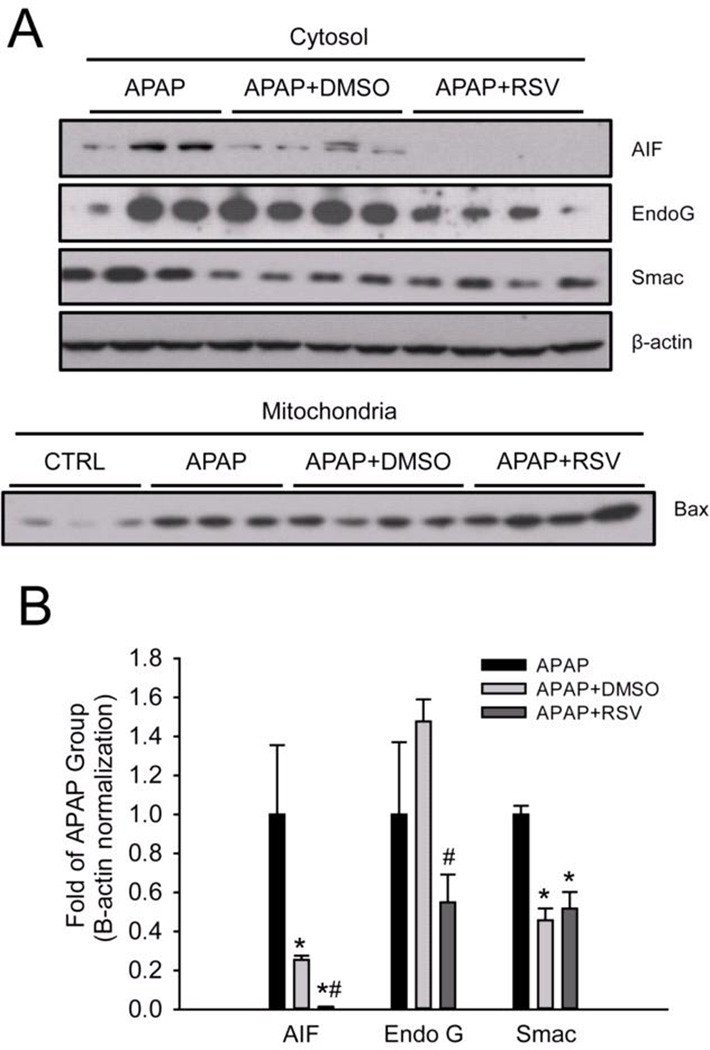
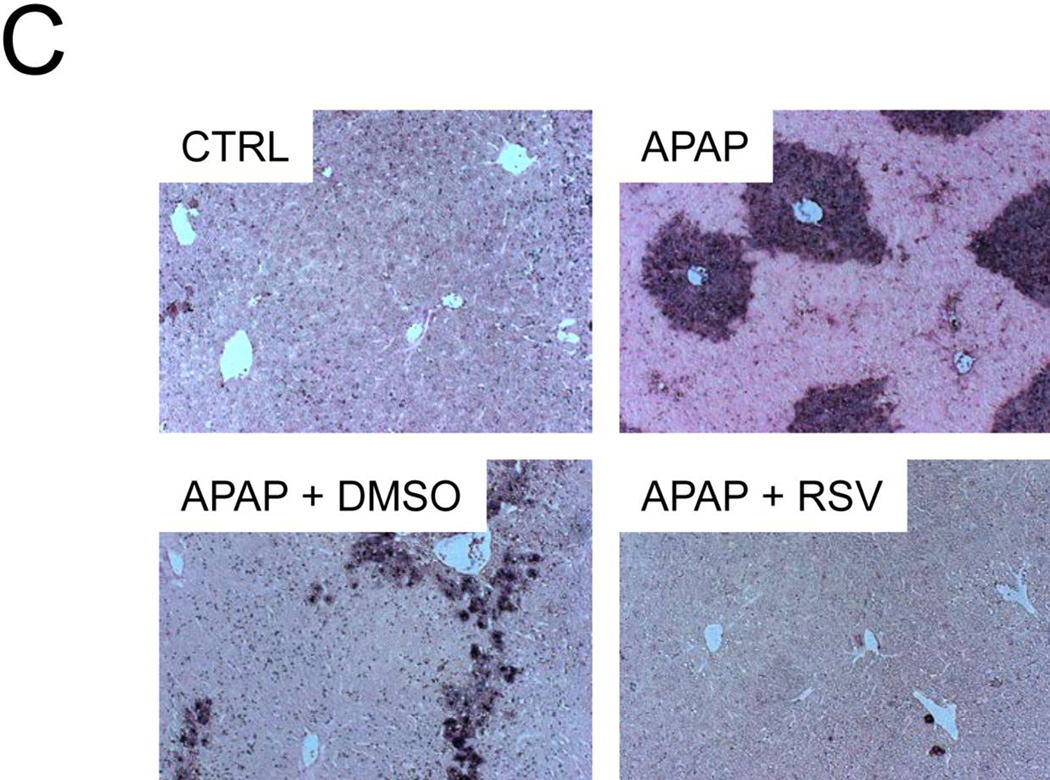
Figure 6. Resveratrol prevents release of endonucleases factor from mitochondria and nuclear DNA fragmentation during acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity.
Mice were treated with 300 mg/kg APAP followed by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle or 50 mg/kg resveratrol (RSV) 1.5h later. Liver tissue was harvested at 6 h post-APAP and mitochondrial and cytosol fractions were isolated. (A) Western blots for apoptosis-induced factor (AIF), endonuclease G (EndoG), and Bax in subcellular fractions. (B) Densitometry. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM for n = 3–4 mice. *P < 0.05 vs. CTRL. #P< 0.05 vs. APAP + DMSO treatment. (C) Nuclear DNA fragmentation in liver tissue sections as visualized by the TUNEL assay.