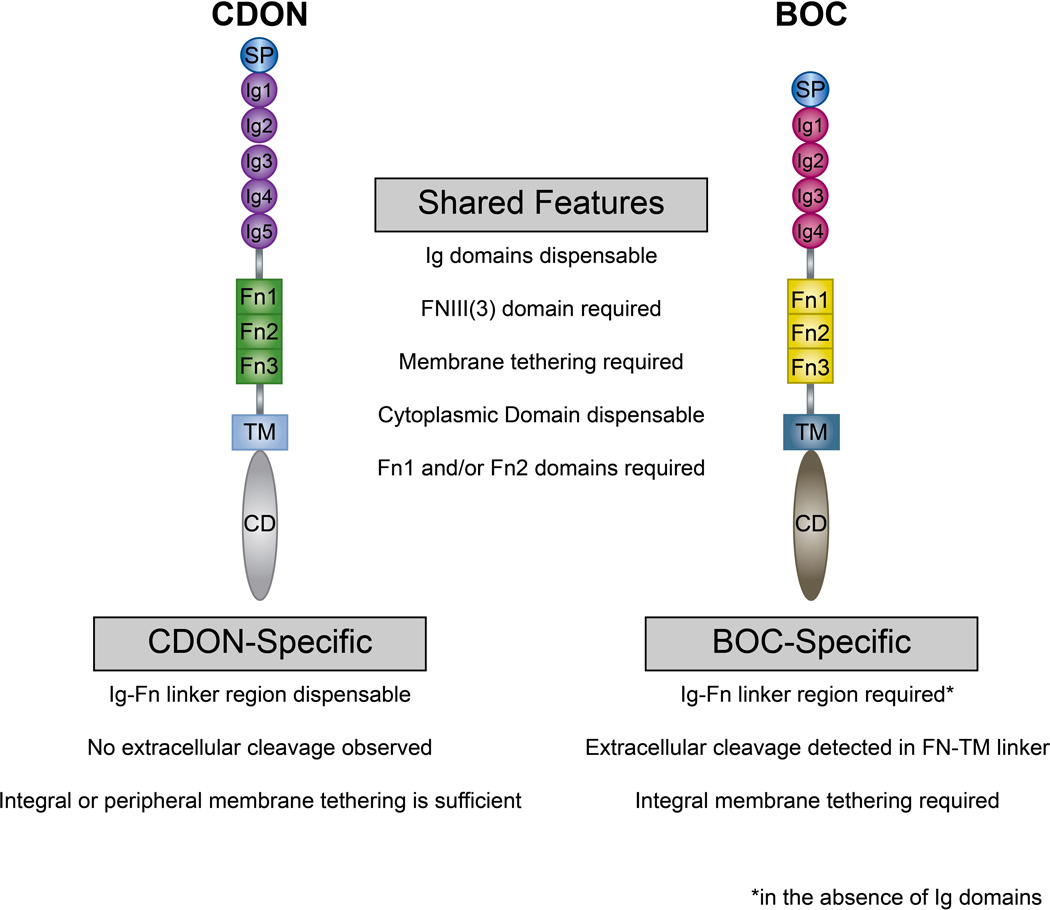
Figure 9. Summary of the structural requirements for CDON and BOC in HH signal transduction.
Schematic summarizing the structural domain requirements for CDON- and BOC-mediated promotion of HH signaling. Shared features are listed in the center, while CDON- and BOC-specific features are listed below each protein. While the IG domains are dispensable, the FNIII domains are essential for both CDON- and BOC-mediated HH signal transduction. In the absence of the Ig domains, BOC requires an additional linker region N-terminal to the FNIII domains, whereas CDON does not require this domain to induce HH signaling. Further, BOC requires integral membrane tethering, whereas CDON effectively drives HH signaling when tethered via either integral or peripheral membrane anchors. BOC also possesses an extracellular proteolytic cleavage site that may regulate its promotion of HH signaling. Notably, the cytoplasmic domains of both CDON and BOC are dispensable for the promotion of HH signaling during neural tube patterning.