Fig. 6.
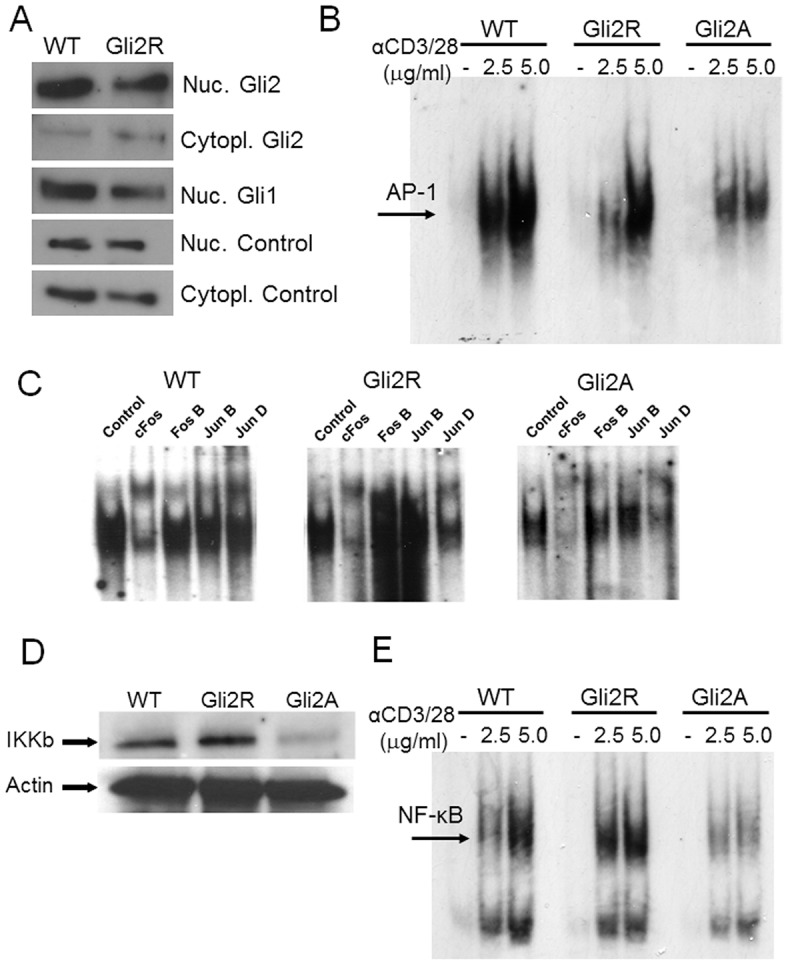
Gli2A-driven transcription attenuates expression and DNA-binding activity of key T-cell transcription factors. (A) Western blotting as in Fig. 1A on extracts from purified CD4+ cells from WT and Gli2R mice. (B) AP-1 activity (arrow) was assessed by EMSA in lymphocytes from WT (n=3), Gli2R (n=3) and Gli2A (n=3) mice activated with 1.25, 2.5 and 5 µg/ml plate-bound anti-CD3/CD28. (C) Supershift assays were performed with anti-Fos and anti-Jun antibodies following EMSA. (D) Protein expression of the IKKβ subunit was assessed by western blotting of CD4+ cell lysates from WT (n=3), Gli2R (n=3) and Gli2A (n=3), anti-actin blotting was performed as the loading control. (E) NFκB activity was probed by EMSA as described above, where cells were activated with 2.5 µg/ml or 5 µg/ml anti-CD3/CD28 as indicated.
