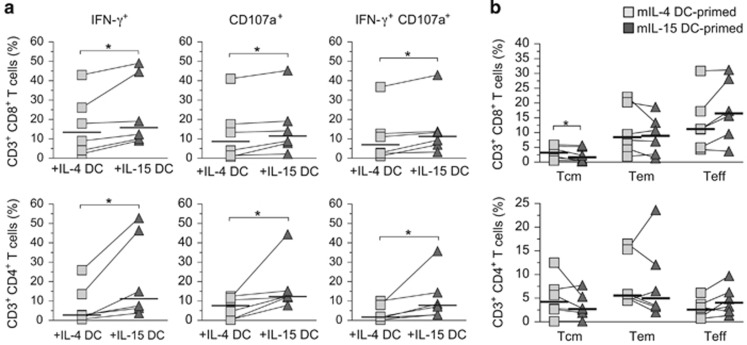
Figure 3.
Increased CMV-specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell recall responses induced by IL-15 DCs. (a) Analyses of Ag-specific effector activities of memory T cells against CMV pp65. mDCs were pulsed with CMV pp65 pooled peptides and incubated with autologous T cells for 16 days. The percentages of specific responding effector T cells producing IFN-γ and CD107a are presented based on results of intracellular staining and flow cytometry. Donor-paired T-cell responses after IL-4 DC (gray squares) versus IL-15 DC stimulation (dark triangles) are depicted by the lines connecting the squares to triangles. Median responding T-cell percentages are indicated by the horizontal bars and statistically significant differences (*) determined by two-tailed, Wilcoxon's matched-pairs signed-rank test with P-value ⩽0.05 (n=6) are shown. (b) Analysis of memory and effector CD4 and CD8 T-cell population distribution in a CMV pp65-primed PBL recall Ag stimulation assay. Central memory (Tcm), effector memory (Tem) and Teff T cells were identified based on characteristics of surface markers, CD45RA, CD27, CD28, CD62L and CCR7, in addition to CD3, CD4 and CD8 by flow cytometry as described previously.20 Donor-paired T-cell responses after IL-4 DC- (gray squares) vs IL-15 DC stimulation (dark triangles) are depicted by the lines connecting the squares to triangles. Median responding T-cell percentages are indicated by the horizontal bars and statistically significant differences (*, n=6) are shown (n=6).