Fig. 2.
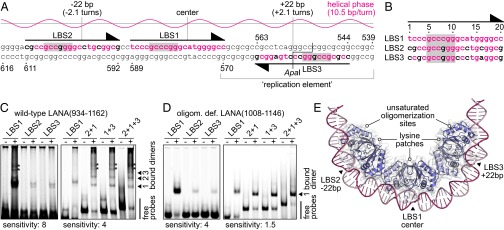
The three LANA binding sites of the KSHV minimal replicator. (A) Sequence of the minimal replicator with the helical phase for standard B-DNA shown above. The primary sites of DNA recognition are shaded in gray. Nucleotide positions identical to those in LBS1 are shown in red letters. Sequence numbering corresponds to a previous study (44) (GenBank: U86666.1). (B) Sequence alignment of the three LANA binding sites. Sequence numbering is as in Fig. 1. (C) EMSA using wild-type LANA(934–1162) (+) or GST as a control (−). An interpretation of the band patterns is provided on the right. Bands of unknown composition are marked with asterisks. These bands may reflect complexes with DNA bound to the lysine patch of LANA (compare Fig. 3). The left gel was exposed with higher sensitivity to visualize the weak bands of the low-affinity core sites. (D) EMSA using the oligomerization-deficient LANA(1008–1146) mutant (+) or GST as a control (−). An interpretation of the bands is provided on the right. The left gel was exposed with higher sensitivity. (E) Model of three LANA dimers bound to the minimal replicator, assuming that binding to LBS2 and LBS3 is structurally similar to LBS1.
