Figure 3.
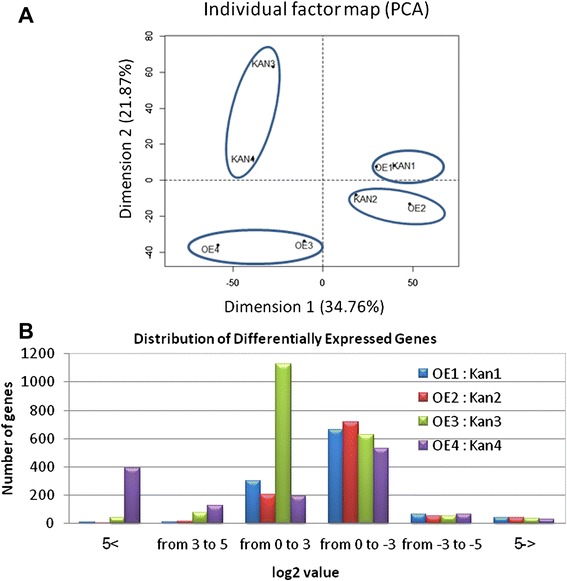
Distribution of differentially expressed genes. (A) Three-dimensional representation according to principle component analysis (PCA) of the differential gene expression data of eight treatments used in the RNA-Seq analysis (as implemented in JMP Genomics 5.1). Kan roots are root samples of vector 11.5 carrying the kanamycin-resistance gene (Kan control roots) and OE roots are mj-far-1.1 lines overexpressing mj-far-1 (OE roots). In this analysis, samples with similar expression profiles lie closer to each other than those with dissimilar profiles. Axes 1 and 2 show robust class separation into four major groups: Kan1 and OE1; Kan2 and OE2; Kan3 and Kan4; and OE3 and OE4. At the early time points (noninoculated and 2 DAI) the infection itself is responsible for most of the transcriptional variance. However, at 5 and 15 DAI, mj-far-1 is the variable responsible for most of the transcriptional variance among treatments with infection playing a lesser role. (B) Distribution of up- and downregulated differentially expressed genes and their fold change over all comparisons made between OE and Kan root lines.
