Figure 1.
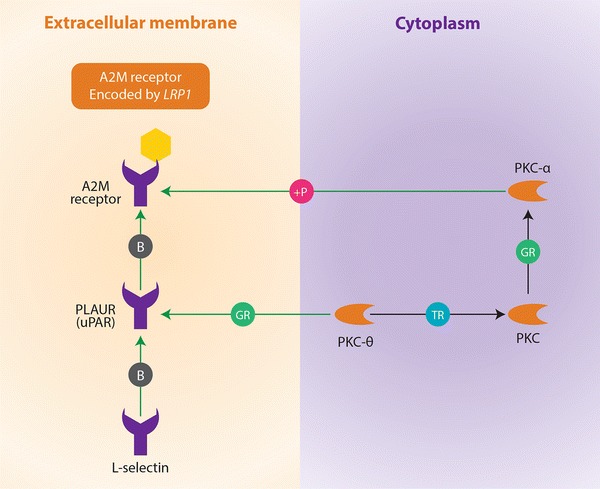
Network analysis of candidate genes involving LRP1 and its potential role in autoimmunity. The network is showing the mechanisms by which protein kinase molecules activate the A2M receptor encoded by the LRP1 gene. The protein highlighted with a hexagonal yellow dot is formed from one of the genes that were identified from the preliminary filtration strategies and used as an input list for the network-building algorithm (in this case gene was LRP1). The cellular locations (i.e., cytoplasm and extracellular membrane) of the interacting molecules, which in this case include protein kinases and the A2M receptor is given. Also included are the mechanisms by which one molecule interacts with another. P phosphorylation, B binding, GR group relation, TR transcriptional regulation. The effect of these mechanisms is denoted in the colour of the symbols corresponding to the respective nodes is as follows: pink activation (by phosphorylation), grey activation (by binding), blue activation (by transcriptional regulation), green unspecified effect due to group relation.
