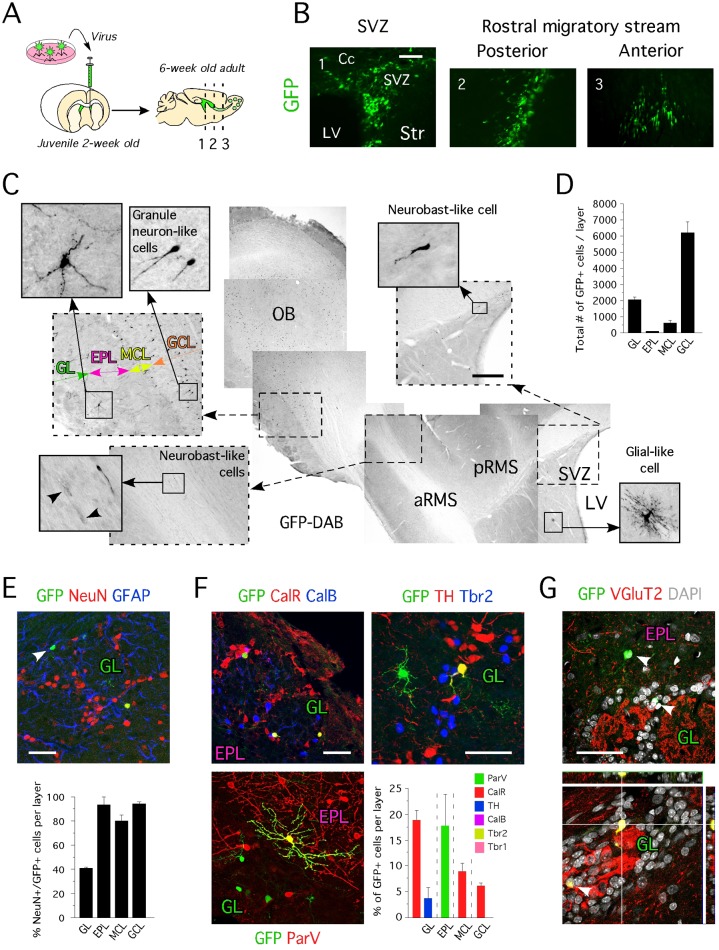
Fig 4. Identity of OB newborn neurons originating from the SVZ of 2 week-old animals.
A- Cartoon illustrating the approach used for in vivo delivery of GFP, Ngn2 and ND1 in the SVZ of juvenile animals. B- Location of cells transduced with GFP virus 2 weeks post-injection revealed by immunohistochemistry for GFP. C- Location of cells transduced with GFP virus 4 weeks post-injection revealed by immunohistochemistry for GFP. D- Total number of GFP cells in specific layers of the OB (GL: 2070 ± 138 cells, EPL: 98 ± 12 cells, MCL: 621 ± 156 cells and GCL: 6242 ± 667 cells). E- Mature and immature GFP+ neurons can be identified in the glomerular layer. Percent of GFP+ cells expressing NeuN in the GL (40.7% ± 0.5%), the EPL (93.3% ± 6.6%), the MCL (80% ± 5%) and the GCL (94.1% ± 1.4%). F- Neuronal identity of GFP+ cells located in the GL, the EPL, the MCL and the GCL revealed by immunohistochemistry for ParV, CalR, TH, CalB, Tbr2 and Tbr1 (as % of GFP) shows absence of newborn TH+ dopaminergic and Tbr2+ and Tbr1+glutamatergic neurons in 2-week old injected animals. G- Immunohistochemistry for VGluT2 on sagittal section of 6-week old animals injected with GFP virus confirms the existence of VGluT2- (upper panel) and VGluT2+ (lower panel) OB newborn neurons originating from the SVZ of 2-week old animals. A to G- Cc = corpus callosum, Str = striatum, SVZ = subventricular zone, MCL = mitral cell layer, pRMS = posterior rostral migratory stream, aRMS = anterior rostral migratory stream, GL = glomerular layer, EPL = external plexiform layer, MCL = mitral cell layer; GCL = granule cell layer, LV = lateral ventricle, OB = olfactory bulb. Values shown as mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 animals. Scale bars: 50 μm (B and E-G), 200 μm (C).