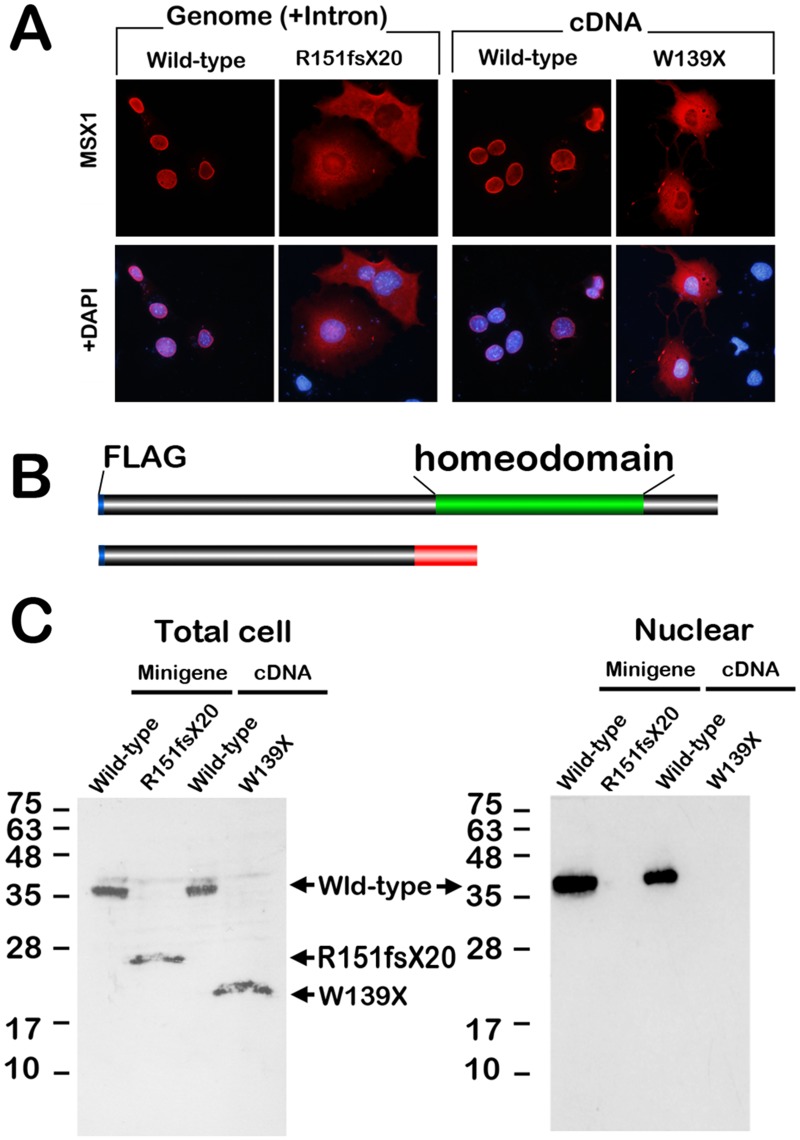
Fig 4. Characterization of the gene product of the MSX1 gene with the c.452-9G>A substitution.
(A) Immunolocalization of FLAG-tagged MSX1 protein in transfected COS7 cells. Nuclear translocation (wild-type) is disrupted by c.452-9G>A substitution in the intronic region (mutant). A diffuse signal is also observed in the transfectant of W139X MSX1, which is a C-terminal truncated mutant. (B) Schematic repetitions of wild and mutant MSX1 protein. The mutant MSX1 protein lacks the homeodomain (green cylinder in wild-type MSX1). Blue cylinder, FLAG tag; red cylinder, unrelated peptide generated by the insertion caused by the c.452-9G>A substitution. (C) Western blotting of cell lysate prepared from total cells (left) or nuclear fractions (right) of COS7 transfected with the MSX1 minigene (FLAG tagged wild-type and c.452-9G>A) or cDNA (FLAG tagged wild-type and W139X) expression vectors. The molecular masses of the R151fsX20 and W139X MSX1 proteins are lower than that of wild-type MSX1.