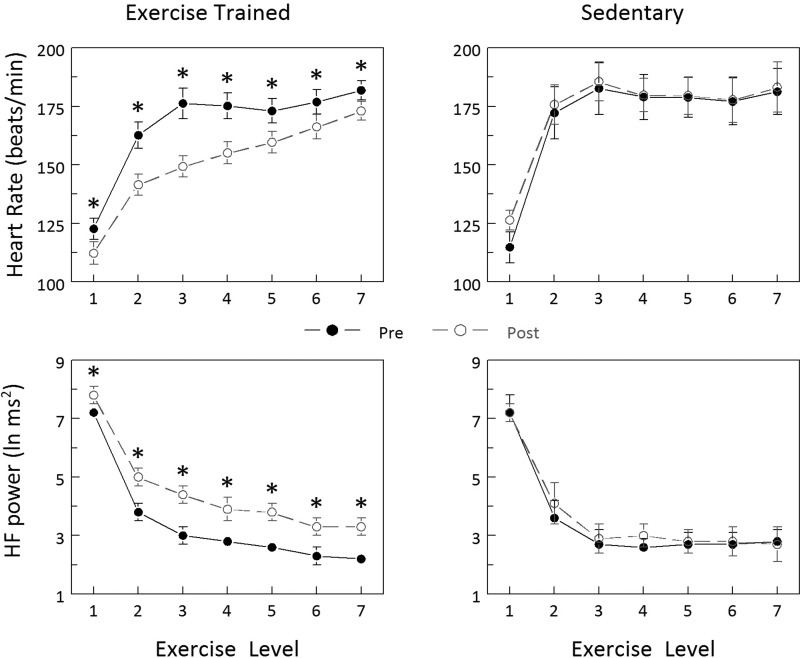
Fig. 1.
Effect of exercise training on heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) responses to submaximal exercise. Exercise training decreased HR and increased HRV (HF power) at each exercise level, whereas these variables did not change in sedentary animals. Exercise levels: 1, 0 kph/0% grade; 2, 4.8 kph/0%; 3, 6.4 kph/0%; 4, 6.4 kph/4%; 5, 6.4 kph/8%; 6, 6.4 kph/12%; 7, 6.4 kph/16%. Pre and Post indicate, respectively, before and at the end of the 10- to 12-wk study period. HF power, high-frequency component of the R-R interval variability (0.24 to 1.04 Hz). *P < 0.01 Pre vs. Post values.