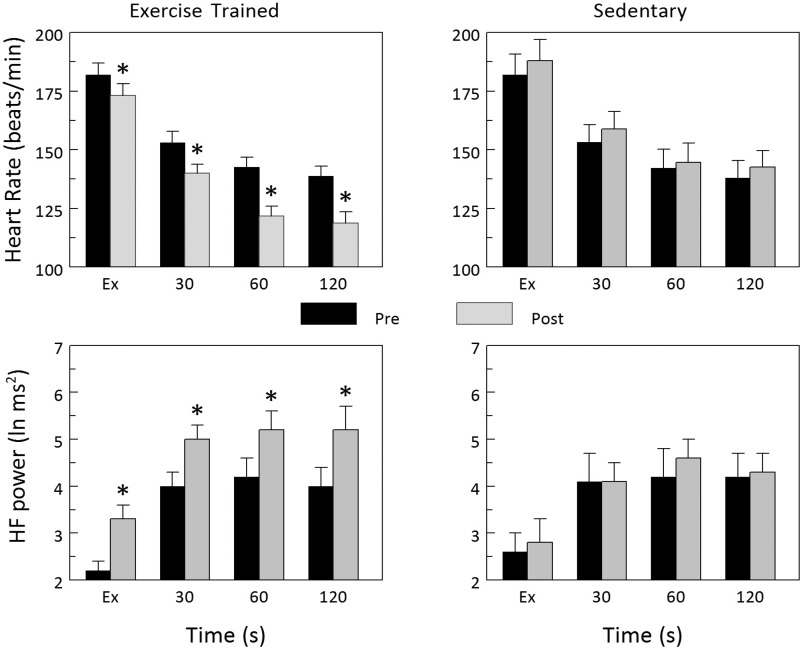
Fig. 3.
Effect of exercise training on HR and HRV responses to the termination of submaximal exercise. Both HR and the high-frequency component of the R-R interval variability (HF power) returned toward baseline values much more rapidly after completion of the 10- to 12-wk exercise training protocol. In contrast, the recovery from submaximal exercise was not altered in the sedentary group. These data suggest that exercise training-mediated increases in HR recovery following the termination of exercise resulted from a more rapid reactivation of cardiac parasympathetic regulation. Data were averaged over each 30-s period beginning with the last 30 s of the submaximal exercise test (time = Ex) and for the first 120 s following the termination of exercise. *P < 0.01 pre vs. post values.