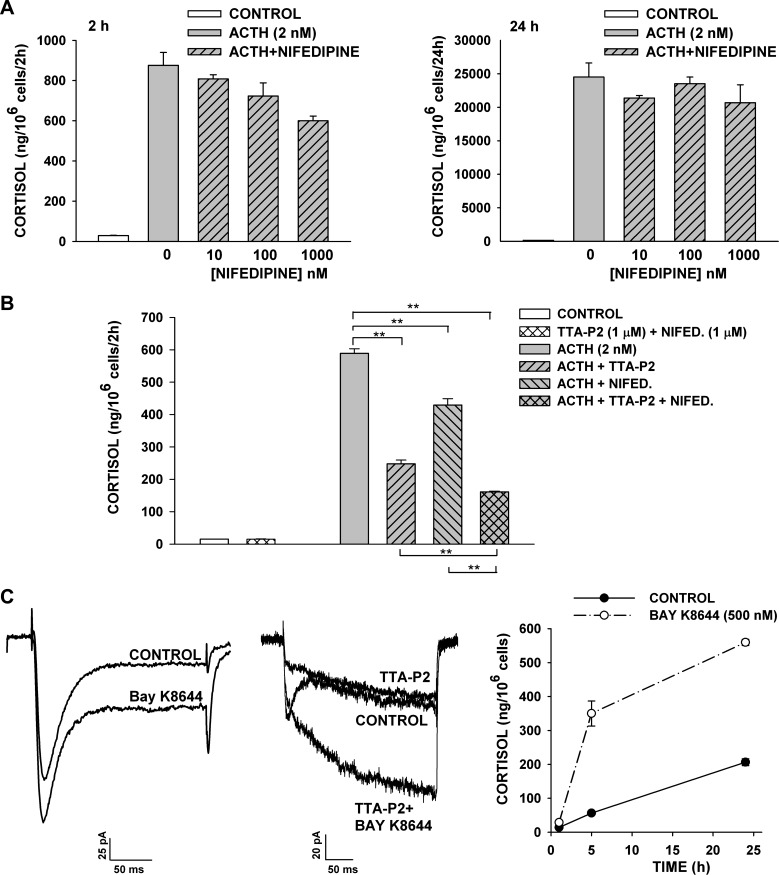
Fig. 10.
Effect of nifedipine, TTA-P2, and BAY K8644 on cortisol secretion and L-type currents. At 24 h after bovine AZF cells were plated, medium was aspirated and replaced with defined medium without (control) or with ACTH, nifedipine, TTA-P2, or BAY K8644. Samples containing TTA-P2 or nifedipine were pretreated with agent alone for 30 min prior to addition of ACTH. Medium was collected at 2 and 24 h, and cortisol concentration was determined by enzyme immunoassay. Values are means ± SE of duplicate determinations from triplicate plates. A: cortisol from media samples collected 2 h and 24 h after no treatment (control) or treatment with ACTH (2 nM) or ACTH + nifedipine (1-1,000 nM). P < 0.007 for 1,000 nM nifedipine at 2 h. B: cortisol from media samples collected 2 h after no treatment (control) or treatment with TTA-P2 (1 μM) + nifedipine (1 μM), ACTH (2 nM), or ACTH (2 nM) + TTA-P2 (1 μM) and/or nifedipine (1 μM). **P < 0.001 for TTA-P2, nifedipine, and TTA-P2 + nifedipine inhibition of ACTH-stimulated secretion. C: BAY K8644 increases rapidly and slowly activating components of L-type current in AZF cells and stimulates cortisol secretion. Ca2+ currents were recorded in 10 mM Ba2+ in response to voltage steps to −5 mV, applied from a holding potential of −80 mV, before superfusion of the cell with 1 μM BAY K8644 (left) or 2 μM TTA-P2 followed by 2 μM TTA-P2 + 1 μM BAY K8644 (middle). Right: cortisol measured from media samples collected 0–25 h after no treatment (control) or treatment with BAY K8644 (500 nM).