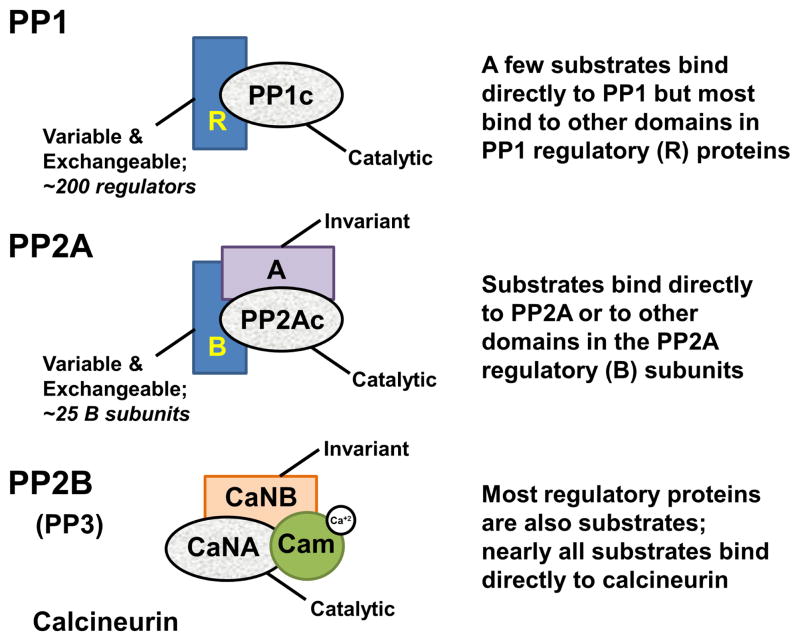
Figure 1. Conservation of PSP catalytic domains.
PP1 (top), PP2A (middle) and PP2B/Calcineurin (bottom) have a highly conserved catalytic domain (grey). PP1 interacts with ~200 distinct regulatory proteins (R; blue), which function as inhibitory and targeting proteins. PP1 substrates bind directly to PP1, bind to other domains that are part of the PP1 regulatory proteins to enhance dephosphorylation or are dephosphorylated because PP1 is localized in proximity to the substrate via its targeting proteins. The catalytic domain PP2Ac interacts with an invariant A subunit and ~25 regulatory B subunits to achieve substrate specificity in a manner similar to that of PP1. Calcineurin (CN), on the other hand, is regulated by calcium, which is required for activation. CN binds directly to its substrates via protein interaction motifs that are also used by regulatory proteins.