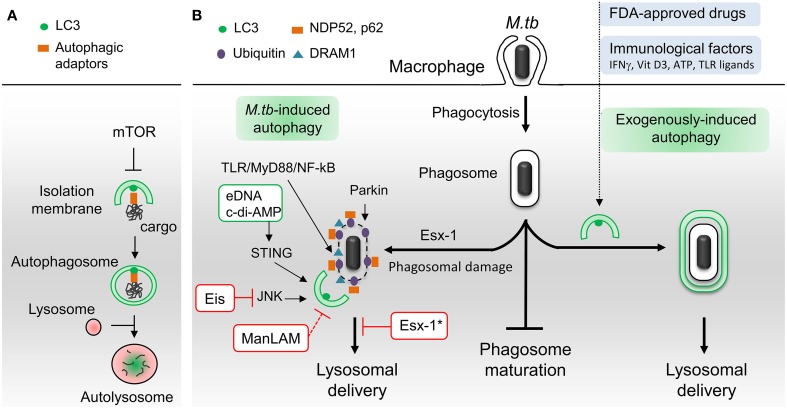
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of autophagic pathways and modulators involved in M. tuberculosis infection. (A) Principal steps in autophagosome biogenesis and maturation (i.e., lysosomal delivery). Autophagy begins with the formation of an isolation membrane that grows to enclose cytoplasmic cargo marked with autophagic adaptors. Once sealed, the autophagosome fuses with lysosomes to allow degradation of sequestered cargo. Numerous signaling pathways regulate autophagy including master repressor Ser/Thr kinase mTOR. (B) M.tb-autophagy interaction in macrophage. Following phagocytosis, M.tb resides in a vacuole called phagosome and blocks phagosome maturation. Several immunological and pharmaceutical autophagy inducers can restore delivery of M.tb to lysosomes. Esx-1-secreting M.tb promotes phagosome damages which trigger ubiquitination, recruitment of autophagic adaptors and mycobacterial capture via STING, Parkin and DRAM1. M.tb extracellular DNA (eDNA) and cyclic-di-adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) activate autophagy whereas Eis and ManLAM inhibit this process. Note that ManLAM was not studied in the context of infection. *Esx-1 blocks autophagosome maturation in human dendritic cells. Vit D3, vitamin D3; TLR, toll-like receptor. Green box, M.tb factors activators of autophagy. Red box, M.tb factors inhibitors of autophagy.