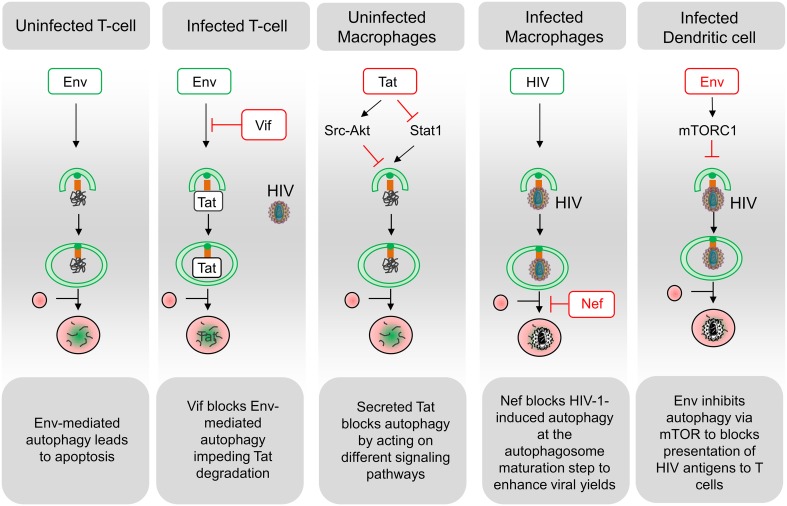
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of interactions between HIV and the autophagy pathway. A complex relationship exists between HIV and the autophagy process in the different targeted cell types. Functional autophagy is an anti-HIV process as it promotes degradation of the viral protein Tat, limits virion production and HIV antigen presentation. However, HIV can block the autophagy pathway at the initiation step (Env in dendritic cells; Tat in uninfected macrophages; Vif in infected CD4 T cells) or at the maturation step (Nef in infected macrophages). Notably, the blockade of autophagy maturation by Nef, in infected macrophages, can be beneficial for HIV. In uninfected CD4 T cells, Env-induced autophagy is a prerequisite for the induction of apoptosis. Viral determinants that are inducers of autophagy are indicated in green, and viral determinants that inhibit this process are indicated in red.