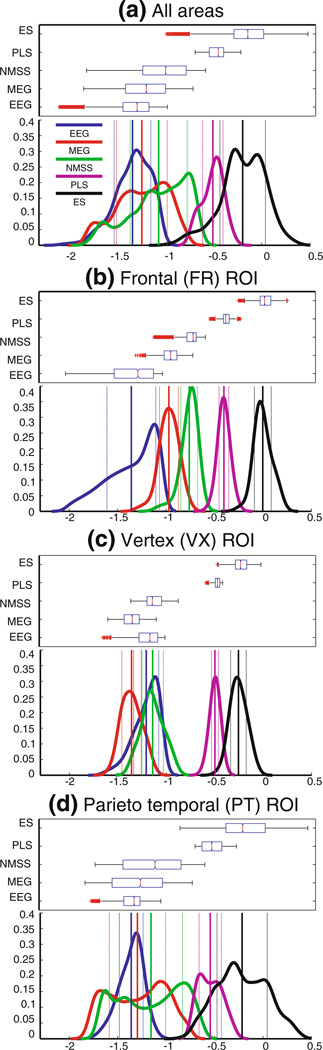
Fig. 5.
Statistical comparison of EEG vs.MEG frequency scaling exponent for all regions (a) and different ROI masks (b, c & d). In each panel, a box-plot on top is accompanied by a nonparametric distribution function in the bottom. In the top graph, the box has lines at the lower quartile, median (red), and upper quartile values. Smallest and biggest non-outlier observations (1.5 times the interquartile range IRQ) are shown as whiskers. Outliers are data with values beyond the ends of the whiskers and are displayed with a red plus sign. In the bottom graph, a Nonparametric density function shows the distribution of EEG, MEG and empty-room-corrected MEG frequency scaling exponents (note that LMSS and WF are not shown here; see the text for description.). Thick and thin vertical lines show the mean and mean ± std for each probability density function (pdf)