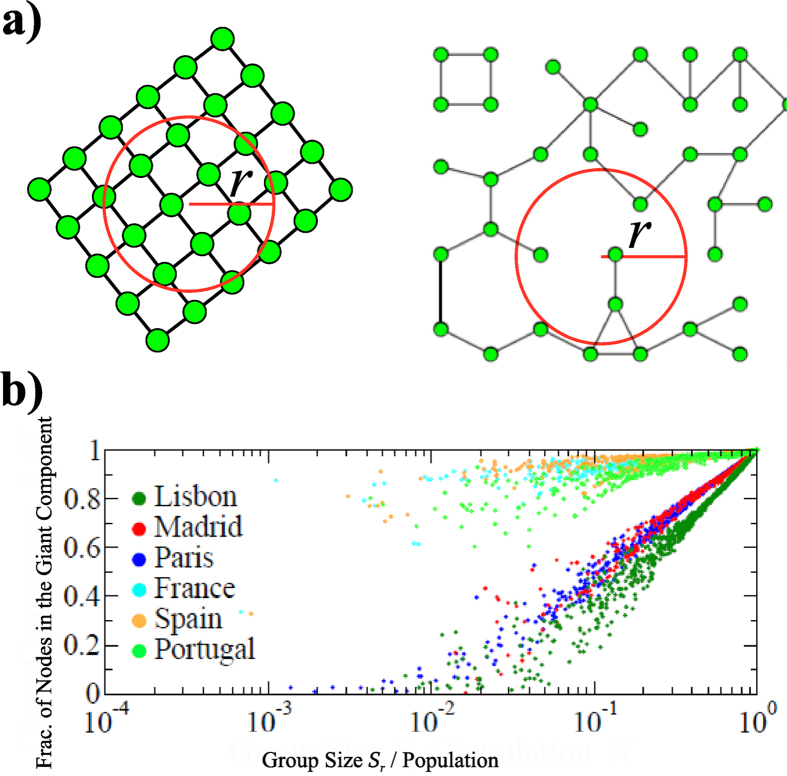
Figure 4.
Short range connectivity (a) In a 2D lattice (left), any geographic ball contains a connected network, however this is not the case for any network (right) where the path between two nodes within a geographic ball might include nodes out of the ball if the network induced by the nodes within the ball is not connected. (b) Fraction of nodes in the giant component as a function of the relative size of the geographic ball for the three capitals compared to the country-wide networks. Each of the 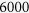 dots in the figure was calculated by selecting 2 nodes
dots in the figure was calculated by selecting 2 nodes 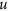 and
and  at random within a city or within the country, extracting the subnetwork defined by the ball whose center is in
at random within a city or within the country, extracting the subnetwork defined by the ball whose center is in 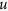 and radius up to
and radius up to  , and identifying the number individuals that belonged to the giant component of such subnetwork.
, and identifying the number individuals that belonged to the giant component of such subnetwork.