Figure 1.
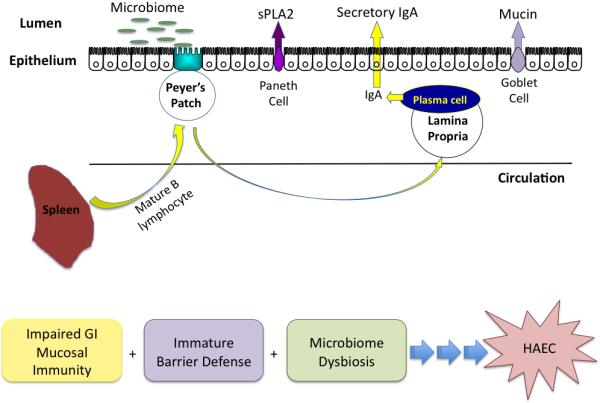
Pathogenesis of HAEC.
Based on recent studies, the etiology of HAEC likely includes impaired mucosal immunity, immature barrier defense and an altered microbiome. These studies suggest that alterations in the intestinal barrier, including goblet cell number and function and Paneth cell function, impaired gastrointestinal mucosal immunity, including B-lymphocyte trafficking or function and secretory IgA production, and dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota may contribute to the development of HAEC.
