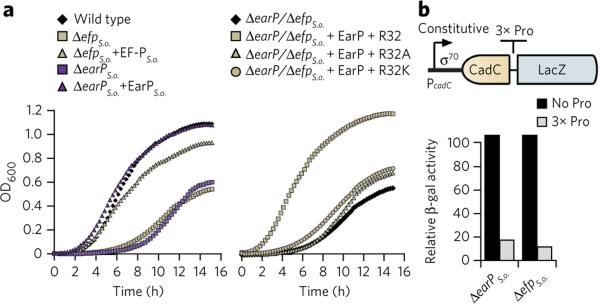
Figure 2. Phenotypic analysis of S. oneidensis MR-1 earP and efp deletion mutants.
(a) Growth of S. oneidensis MR-1 strains. Left, wild-type strains in comparison to ΔefpS.o. and ΔearPS.o. deletion strains and after complementation in trans (+efpS.o., +earPS.o.). Right, the ΔefpS.o. deletion strain and after complementation with plasmids encoding His6 versions of EF-PS.o. (+R32) or the corresponding substitution variants EF-PS.o.R32A (+R32A) and EF-PS.o.R32K (+R32K), respectively. The presented growth curves are average data from three independent data sets, with statistical error below 10%. (b) β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity assay of S. oneidensis MR-1 ΔefpS.o., ΔearPS.o. encoding a constitutively produced LacZ-hybrid without (black bars) or with (gray bars) a polyproline motif (3× Pro). β-galactosidase activity is given in percent and is normalized to the wild-type values. The relative activities are average data from three independent data sets, with statistical error below 10%.