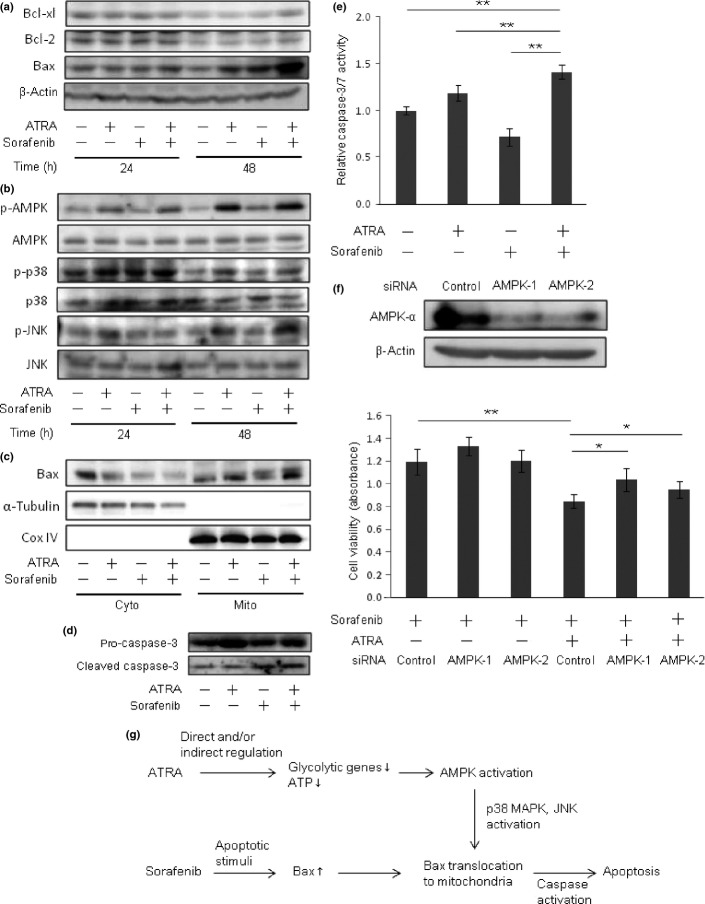
Fig 6.
Combination treatment of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and sorafenib induced apoptosis by enhancing the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. (a) Western blot analysis of Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bax of cells treated with 0.1 μM sorafenib or 10 μM ATRA alone, or in combination, for 24 or 48 h. β-Actin served as a control of protein loading. (b) Western blot analysis of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phospho- (p-)AMPK, p-p38, p38, p-JNK, and JNK. (c) Identification of subcellular localization of Bax. Cytosolic (Cyto) and mitochondrial (Mito) fractions of the cells were analyzed by Western blot using anti-Bax, anti-α-tubulin (cytosolic marker), and anti-Cox IV (mitochondrial marker) antibodies. (d) Detection of pro-caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-3 in cells at 48 h after treatment. (e) Caspase-3/7 activity of the cells at 48 h after treatment. (f) Effect of AMPK knockdown on the viability of cells treated with sorafenib and ATRA. Upper, two siRNAs were validated for the suppression of AMPKα protein expression. Lower, cells were incubated with control- and AMPK-siRNA for 24 h, and then were subjected to the treatment indicated. WST assay was carried out 72 h after treatment. Experiments were run in triplicate and carried out twice on separate occasions. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (g) Illustrative presentation of the mechanism of additional cytotoxicity induced by ATRA on hepatocellular carcinoma cells treated with sorafenib.