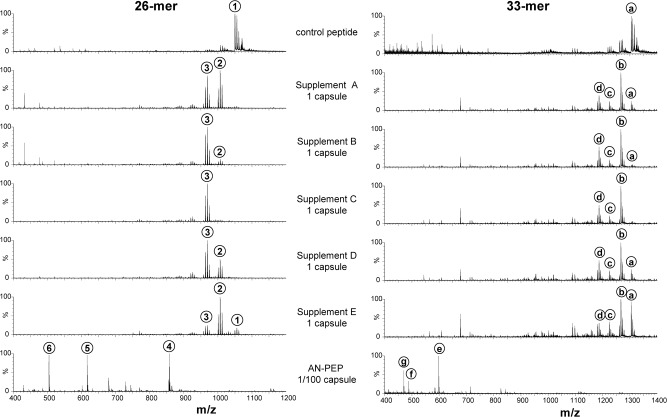
Fig 2. Mass spectrometric analysis of the degradation products of 26-mer and 33-mer peptide by digestive enzyme supplements.
Peptide was incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes at pH 6.0 in the presence of 1 capsule equivalent digestive enzyme supplements. As a control, 1/100 capsule equivalent of AN-PEP at pH 5.0 was also incubated. Peptide reaction products were analyzed by Q-TOF LC-MS and their MS spectra shown in this Figure. The identity of the prominent peptides 1–6 and a-g are given in Table 4. In the case of AN-PEP, small amounts of epitope-containing peptides were observed under these conditions, but they disappear at higher enzyme concentration or prolonged incubation (see Fig 3). The digestive enzyme supplements display comparable activities and remove at most two amino acids from the N-terminus of the 26-mer (peptide 1 (26-mer) is degraded to peptide 2, and then to peptide 3), and three amino acids at most from the 33-mer peptide (peptide a (33-mer) is degraded to b, to c, and then to peptide d).