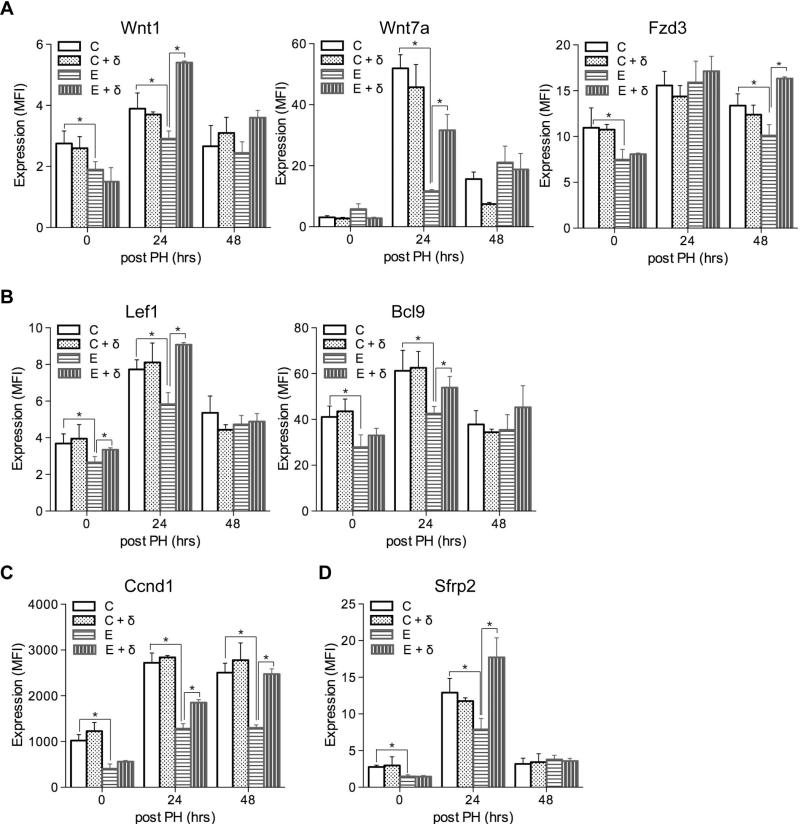
Fig. 5.
Effects of PPAR-δ agonist treatment on hepatic Wnt pathway gene expression following PH in control and chronic ethanol-fed rats. Adult male Long Evans rats were fed with isocaloric liquid diets containing 0% or 37% ethanol for 8 weeks. During the last 3 weeks of the feeding regimen, rats were administered twice weekly i.p. injections of saline or a PPAR-δ agonist. The rats were then subjected to PH and livers were harvested 0, 24, or 48 hours later to measure Wnt pathway gene expression using the Quantigene 2.0 Multiplex Assay. Gene expression levels were indexed in arbitrary mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) units, and results were normalized to a housekeeping gene that was not modulated by PH or liver regeneration. Graphs depict results obtained for (A) Wnt1, Wnt7a, and Fzd3; (B) the Lef1 and Bcl9 Wnt transcription factors; (C) the Ccnd1 Wnt target gene; and (D) the Sfrp2 Wnt ligand binding protein. C, control + saline; C + δ, control + PPAR-δ; E, ethanol + saline; E + δ, ethanol + PPAR-δ. Inter-group comparisons were made by two-way repeated measures ANOVA tests with Bonferroni's pos-hoc test using GraphPad Prism 5. *p < 0.05.