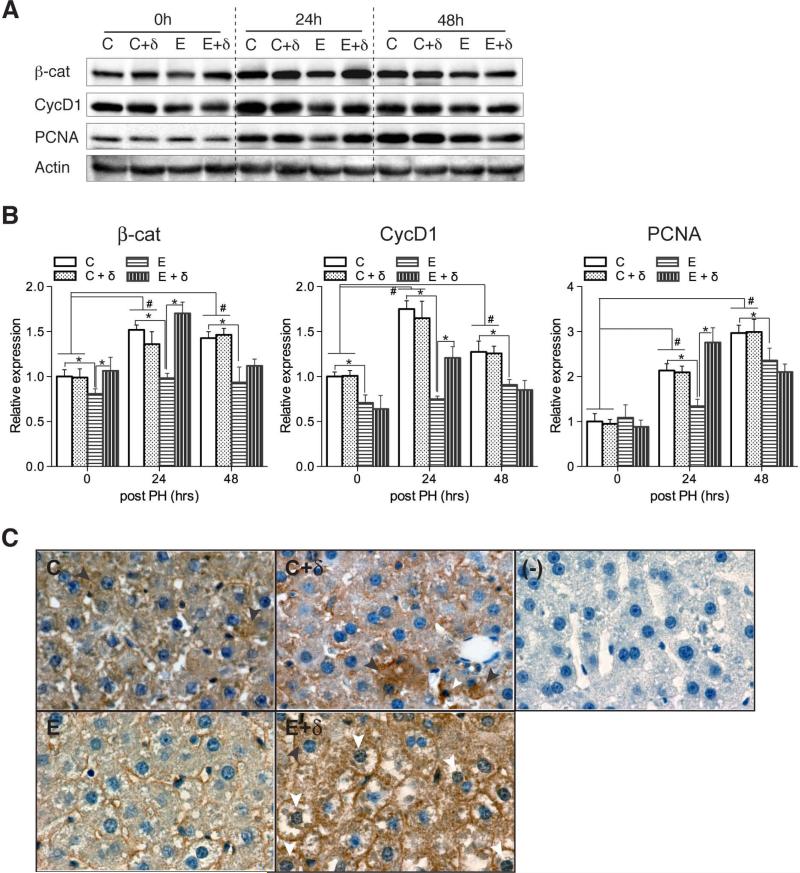
Fig. 6.
Effects of PPAR-δ agonist treatment on hepatic Wnt pathway protein expression following PH in control and ethanol-fed rats. Adult male Long Evans rats were fed with isocaloric liquid diets containing 0% or 37% ethanol for 8 weeks. During the last 3 weeks of the feeding regimen, rats were administered twice weekly i.p. injections of saline or a PPAR-δ agonist. The rats were then subjected to PH and livers were harvested 0, 24, or 48 hours later to measure (A) β-catenin, Cyclin D1, PCNA, and Actin by Western blot analysis. (B) Graphs show relative levels of immunoreactivity (mean ± S.E.M.) normalized to control+vehicle values measured at the corresponding time point. Data were obtained by subjecting the Western blot signals to densitometric analysis (arbitrary units). Signal intensities were normalized to Actin. Inter-group comparisons were made by two-way repeated measures ANOVA tests with Bonferroni's pos-hoc test using GraphPad Prism 5. *, # p < 0.05. (C) Localization of β-catenin by immunohistochemistry. Panels depict representative β-catenin staining of livers from 24 hour post partial hepatectomy. (C) and (C + δ) had cytoplasmic expression (black arrowhead), whereas (E + δ) liver exhibited nuclear localization of β-catenin (white arrowhead).