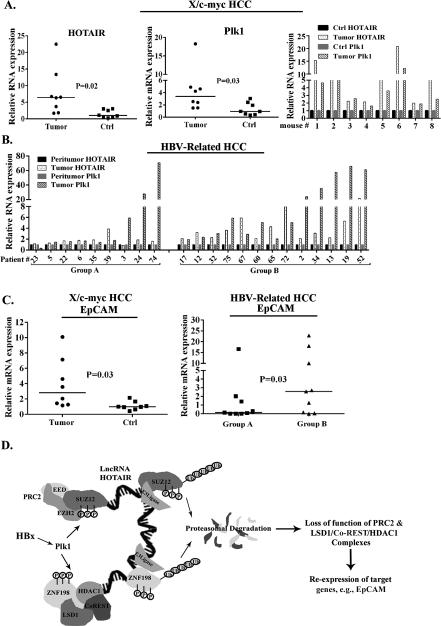
Figure 6. Plk1 and HOTAIR overexpression in liver tumors from X/c-myc mice and HBV-infected patients.
PCR quantification of Plk1 and HOTAIR RNAs using total RNA isolated from A. liver tumors of X/c-myc bitransgenic mice compared to control (Ctrl) RNA (normal mouse liver or peritumoral tissue), shown as box plots or histograms in liver tumors from individual mice. B. PCR quantification of Plk1 and HOTAIR RNAs using RNA isolated from HBV-related HCCs compared to peritumoral tissue. Quantitative PCR reactions were performed in identical triplicates (Plk1 and HOTAIR) using GAPDH as internal control. C. Quantification of EpCAM mRNA in liver tumors from X/c-myc mice (left panel) and HBV-mediated HCCs (right panel), expressed relative to Ctrl RNA. PCR quantification of RNAs from HBV-related HCC samples were performed in duplicates employing PCR arrays, and expressed relative to normal liver (average value from eight patients). p values are shown. D. Model illustrates the mechanism by which HBx-activated Plk1 by phosphorylation signals ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of SUZ12 and ZNF198. HOTAIR accelerates ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of SUZ12 and ZNF198, likely acting as scaffold for recruitment of RNA binding E3 ligases, as described by Yoon et al (41).