Fig. 3.
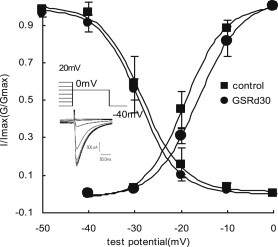
Effect of ginsenoside Rd (GSRd) on steady-state activation and inactivation. For the activation curves, the voltage dependence of the conductance activation variable were fitted to Boltzmann distribution: G/Gmax = 1/{1 + exp[(V − V0.5)/κ]}, where G/Gmax is the ratio of conductances [G = I/(V − Vrev), where Vrev is the reversal potential from each I–V curve)] to maximum conductance (Gmax, measured at 0 mV); V is the membrane potential, V0.5 is the midpoint, and κ is the slope. V0.5 and κ were −19.12 ± 0.68 mV and 4.26 ± 0.78 mV in the control, and −16.26 ± 0.38 mV and 4.61 ± 0.32 mV in GSRd (30 μmol/L). For the inactivation curves, protocol and representative recordings used to assess availability (I/Imax) are shown at lower left. I/Imax were also fitted to Boltzmann distribution. Currents (I) at 0 mV after 1-s conditioning pulses between −50 mV and 20 mV to 0 mV with 250 ms square wave were normalized by maximum current (Imax). V0.5 and κ were −28.34 ± 0.45 mV and 4.41 ± 0.42 mV in the control, and −28.99 ± 0.28 mV and 4.21 ± 0.28 mV after GSRd application.
