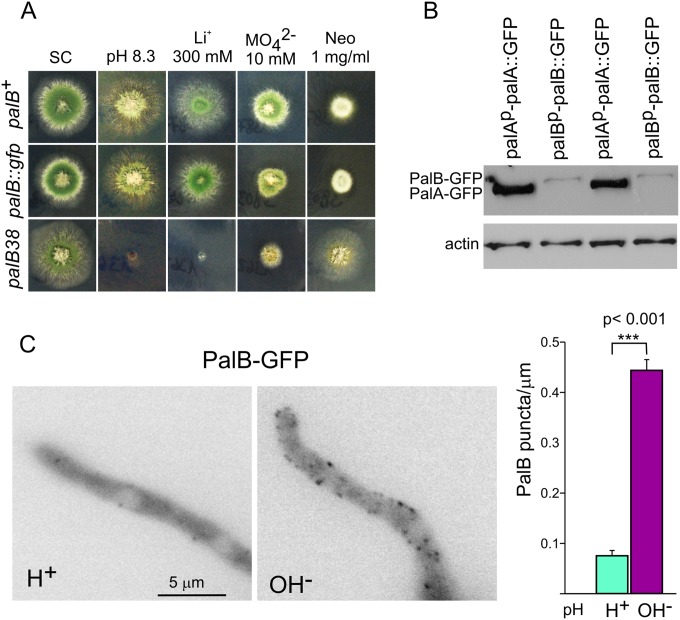
FIG 6.
PalB is recruited to cortical puncta in an alkaline-dependent manner. (A) Diagnostic tests of pH regulation for palB-GFP. The null palB38 mutation prevents growth at pH 8.3 or on 0.3 M LiCl-containing media, and it leads to hypersensitivity to 10 mM sodium molybdate and to resistance to 1 mg/ml of neomycin (Neo). A palB-GFP gene replacement strain grows like the wild type at pH 8.3 and on LiCl and sodium molybdate plates, and it is as sensitive as the wild type to neomycin, indicating that tagging does not impair function. (B) Western blot analysis of cells expressing endogenously tagged PalA-GFP or PalB-GFP. Actin is a loading control. (C) Cells expressing PalB-GFP under the control of alcAp were cultured on ethanol medium at acidic pH and shifted to acidic (H+; pH 5.2) or alkaline (OH−; pH 8.2) pH for 30 min before being photographed. The diagram on the right is a quantitation of the number of cortical structures per micron counted in 32 hyphal tip cells cultured under acidic or alkaline conditions. Error bars are standard errors. The two sets of measurements are significantly different (P < 0.001) as determined with the Mann-Whitney U test.