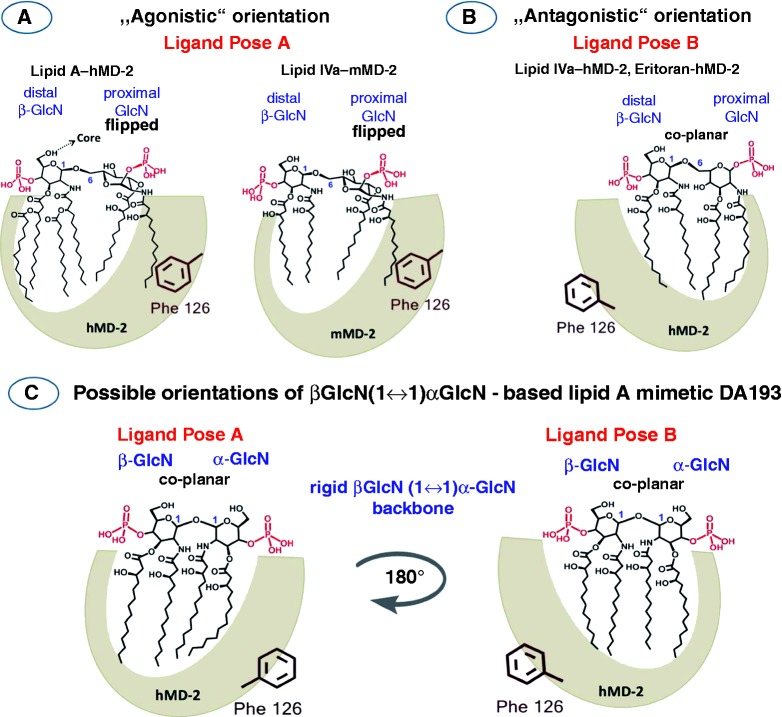
Figure 2.
Orientations of the lipid A ligands within the binding pocket of MD-2. (A) Schematic representation of the orientation of the agonistic ligands resolved in the co-crystal structures: E. coli lipid AhMD-2·TLR4 (PDB code: 3FXI) and lipid IVamMD-2·TLR4 (PDB code: 3VQ1) wherein the proximal (reducing) GlcN ring of the βGlcN(1↔6)GlcN backbone faces the Phe126 loop. Phe126 is shifted inward to stabilize the exposure of the 2N-acyl chain on the surface of MD-2 and to allow the dimerization with the second MD-2*·TLR4* complex. (B) Orientation of the antagonistic ligand lipid IVa hMD-2 (PDB code: 2E59) wherein the distal (non-reducing) GlcN ring faces the Phe126 loop. Phe126 is oriented outwards and exposed to solvent, which prevents the dimerization of two receptor complexes. (C) Two modeled orientations of DA193.