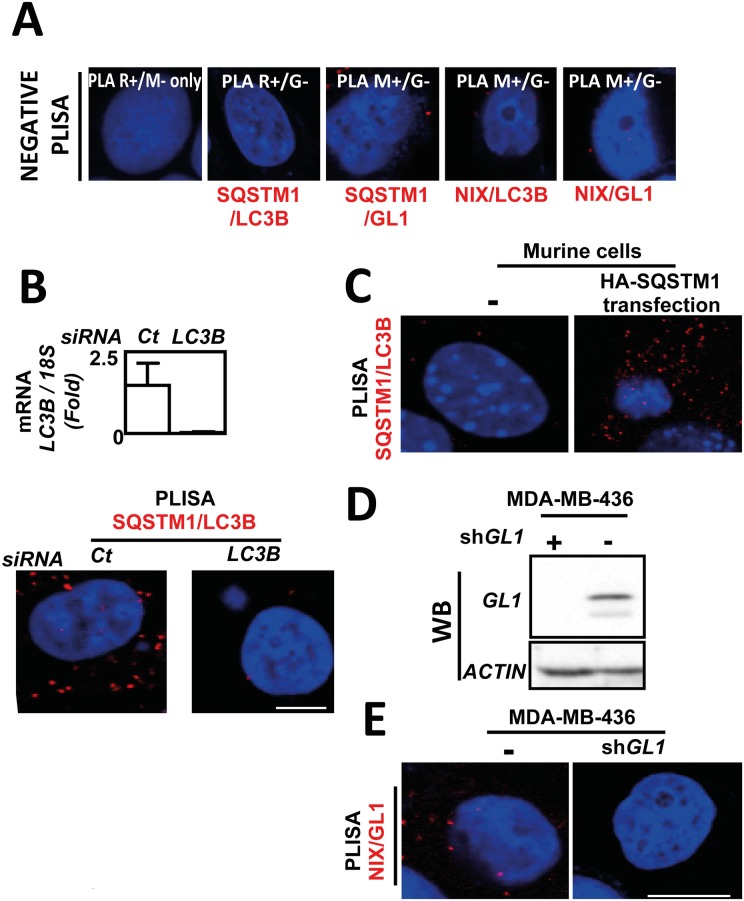
Fig 2. Technical controls demonstrating the specificity of P-LISA signals.
(A) MDA-MB-436 cells were cultured for 24 h at 37°C and 5% CO2. P-LISA were performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. No primary antibodies were added before performing P-LISA with PLA R+ (anti-rabbit) and PLA M- (anti-mouse) (left panel); P-LISA SQSTM1/LC3B was also performed with PLA R+ (anti-rabbit) against LC3B and with PLA G- (anti-goat) unable to recognize SQSMT1 (left panel). Similar controls were performed for P-LISA SQSTM1/GL1, P-LISA LC3B/NIX and P-LISA GL1/NIX. (B) Quantification of LC3B mRNA expression in MDA-MB-436 cells following LC3B siRNA transfection analyzed using qRT-PCR (top panel). Quantification of SQSTM1/LC3 interactions detected by P-LISA in MDA-MB-436 cells transfected or not with LC3B siRNA (bottom panel) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations using rabbit anti-LC3B and mouse anti-SQSTM1 antibodies. (C) Absence of SQSTM1/LC3B P-LISA signals in murine cells since the anti-SQSTM1 antibody is specific of the human SQSTM1 protein and restoration of P-LISA signals when these cells were transfected with a vector coding the human HA-SQSTM1 protein. (D) Absence of GL1 protein was validated using western blotting in MDA-MB-436 cells expressing or not a GABARAPL1 shRNA (E) Quantification of NIX/GL1 interactions was performed by P-LISA in MDA-MB-436 cells expressing or not a GABARAPL1 shRNA using rabbit anti-GL1 and mouse anti-NIX antibodies.