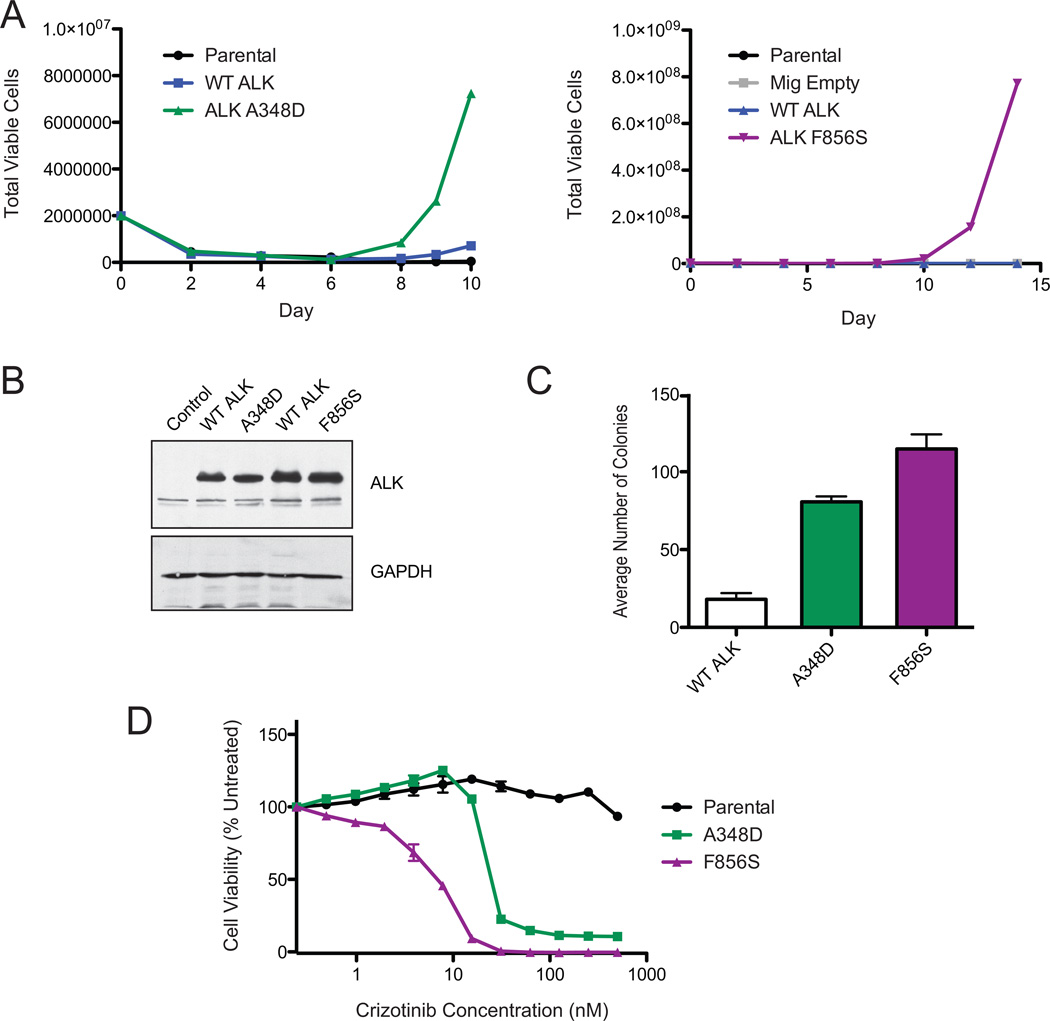
Figure 2. ALK point mutations found in leukemia samples are oncogenic, and sensitive to Crizotinib.
(A) The ALK A348D and F856S mutations transforms the murine Ba/F3 pro-B cell line to cytokine independent growth. Ba/F3 cells expressing WT ALK, ALK A348D, F856S, Ba/F3 cells harboring an empty vector (Mig Empty), or parental Ba/F3s were grown in the absence of the cytokine IL3. Total viable cells are plotted over time. (B) ALK mutations are expressed at the same level as WT ALK. Immunoblot analysis of Ba/F3 cells expressing ALK mutations along with their respective WT ALK controls from each Ba/F3 IL3 withdrawal experiment. GAPDH serves as a loading control. (C) ALK point mutations induce colony formation in mouse bone marrow. Mouse bone marrow cells were infected with retrovirus expressing WT ALK, A348D or F856S and then plated in colony formation medium in the absence of cytokines. The average number of colonies formed from three replicates are shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (D) ALK point mutant expressing Ba/F3 cells are sensitive to Crizotinib. IL3-independent Ba/F3 cells expressing the ALK A348D or F856S mutations were treated with Crizotinib in triplicate. Cell viability was determined using a tetrazolamine based viability assay. Viability is represented as a percentage of the untreated control. The mean of three replicates are shown, along with the standard error.